Introduction
An arteriosclerotic occlusive disease in lower limbs causes ulcer and necrosis below occlusive areas1). This disease is treated by reperforating procedures or vessel replacing operations2,3). After these treatments, Several problems such as pain, coldness, numbness and edema may occur. These problems are called post-reperfusion syndrome(PRS). To this day, Pletaal(cilostazole) is used to reduce the symptoms of PRS4,5). But the conventional therapy is not sufficient to treat PRS.
Cardiotonic Pills(CP) are the complex of herbal medicines, composed of Saliviae Miltiorrhizae Radix, Notoginseng Radix and Borneolum6). CP is uesd to treat anginapectoris, coronary arteriosclerosis, hyperlipidemia and others7,8). To evaluate the effects and safety to PRS by CP with Pletaal, we designed this study by random allocation and comparison to control group.
Objects and Methods
1. Objects
This study was approved by the IRB of Daegu catholic hospital and performed at Daegu catholic medical center.
The objects were the patients of arteriosclerotic occlusive disease treated by reperforating procedures or vessel replacing operations. We selected objects according with the inclusion and exclusion criteria and agreeing to the consent form. We divided the patients by two groups in the course of randomized allocation. One(control group) is treated by Pletaal(cilostazole), the other(CP group) is by Pletaal with CP. Control group was 14 persons(male-11, female-3), and CP group was 13 persons(male-12, female-1). the average of age was 70.21 years in control group, and 68.15 years in CP group(Table 1).
2. Methods
Control group was treated by Pletaal(100 mg) twice a day, CP group was treated by Pretaal(100 mg) twice a day with CP(10 pills) three times a day for 8 weeks.
We primarily evaluated the outcomes by visual analogue scale(VAS) of pain, coldness, numbness, and edema, secondarily hematologic tests. We evaluated the outcomes at first day, and the day of 2 weeks, 4 weeks and 8 weeks.
Results
1. Primary endpoints
(1) Pain
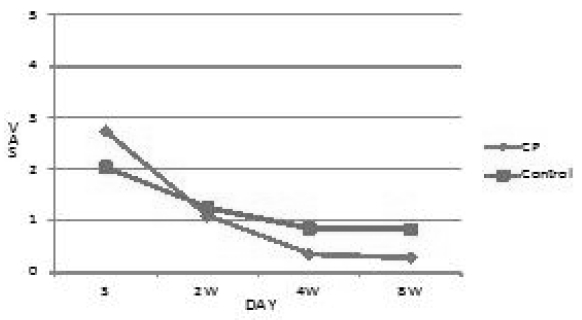
The VAS of control group were 2.036 at first, 1.245 at 2 weeks later, 0.857 at 4 weeks later and 0.833 at 8 weeks later. CP group were 2.731 at first, 1.091 at 2 weeks later, 0.357 at 4 weeks later and 0.283 at 8 weeks later. CP group showed significant decrease of the VAS of pain compared with control group as p<0.05.(Table 2, Fig. 1)
(3) Numbness
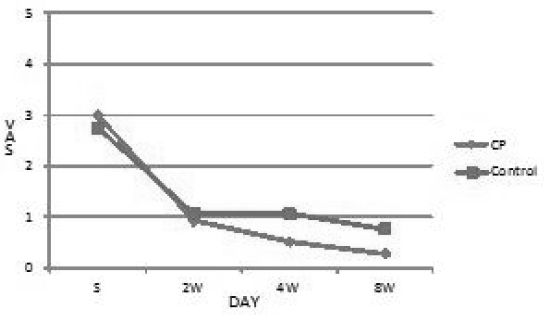
The VAS of control group were 2.75 at first, 1.073 at 2 weeks later, 1.071 at 4 weeks later and 0.778 at 8 weeks later. CP group were 3.000 at first, 0.936 at 2 weeks later, 0.529 at 4 weeks later and 0.283 at 8 weeks later. CP group showed decrease of the VAS of numbness but not significant.(Table 2, Fig 3)
(4) Edema
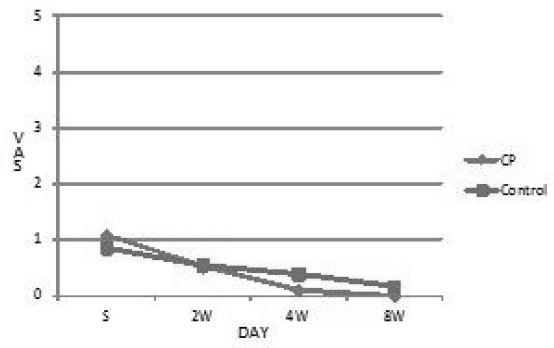
The VAS of control group were 0.857 at first, 0.545 at 2 weeks later, 0.386 at 4 weeks later, and 0.167 at 8 weeks later. CP group were 1.077 at first, 0.518 at 2 weeks later, 0.100 at 4 weeks later, and 0.000 at 8 weeks later. CP group showed decrease of the VAS of edema but not significant.(Table 2, Fig 4)
2. Secondary endpoints
(1) Hematologic tests
The results of hematologic tests were compared with first time and 8 weeks later. The items of hematologic tests were WBC, RBC, Hb, Hct, Platelet, PT(INR), aPTT, AST, ALT, BUN and creatinine.
The results of all groups were within normal limit and no significant changes between first time and 8 weeks later.(Table 3)
Discussion
An arteriosclerotic occlusive disease in lower limbs may cause ulcer or necrosis, in a worse case, amputation is required1,2). To treat this disease, Reperforating procedures or vessel replacing operations is commonly done3). However, the ischemia of peripheral small vessels can not be covered by procedure or operations. Because of this reason, anticoagulant therapy is commonly used after operation.
Pletaal(cilostazole) is a antiplatelet agent that is commonly used in the peripheral artery disease and can improve walking distance9). Cilostazole is selective type III phosphodiesterase inhibitor10,11). It has the effects of anticoagulaton and vasodilatation11). If there are no contraindication, Plettal is generally used after reperforating procedures.
After operations, several problems may occur such as pain, coldness, numbness and edema. Those problems are called post-reperfusion syndrome(PRS). PRS can cause walking problems and several disorders such as insomnia and depression, so it can lower the quality of patient’s life. Because the conventional therapy was not sufficient to treat PRS, we tried to carry the new type of methods.
In Korean medicine, extravasated blood causes pains and sensory problems, so the therapy of blood-activating and stasis-dispelling can kill pains and relieve sensory problems. Because pain is the major part of PRS, blood-activating and stasis-dispelling herbs may relieve the symptoms of PRS.
Before we started this clinical trial, we had evaluated the pharmacokinetics interaction between CP and Plettal in rats. The result suggests that co-administration of CP and Plettal may not cause interactions12).
To relieve PRS and improve the quality of patient’s life, we designed the integral model of Korean and western medicine. We performed clinical trial using CP with Pletaal. CP are composed of Saliviae Miltiorrhizae Radix, Notoginseng Radix and Borneolum. There were several studies about anginapectoris, neuroprotective effects, lipid-lowering effects and cerebral blood flow treated by CP6–8). They have effects of blood-activating, stasis-dispelling and lipid-lowering, so we thought that CP can be used for PRS.
We designed that one group(control group) is treated by only Pletaal, the other(CP group) is by Pletaal with CP. Control group is consist of 14 persons and CP group is 13 persons. We primarily evaluated the effects on relieving tht symptoms of PRS by VAS of pain, coldness, numbness and edema. We compared each group at first day, 2 weeks, 4 weeks and 8 weeks later by multiple comparison. Secondarily evaluate the safety by hematologic tests.
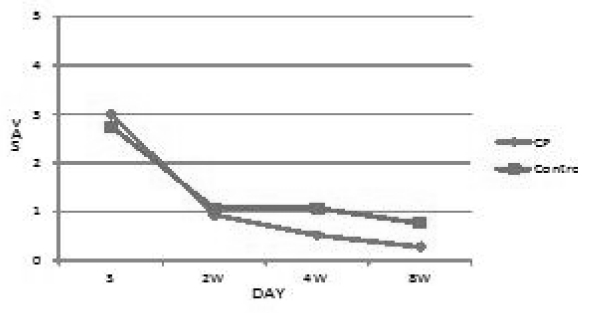
In the results, coldness, numbness and edema were reduced at both groups. In CP group, the VAS dropped more sharply than control group, but not significant by multiple comparison. Otherwise, there was significant reduction of VAS on pain(p<0.05) by multiple comparison. Because pain is the major part of PRS, it is meaningful that the therapy of Pletaal with CP can relieve pain significantly. I think that the blood-activating and stasis-dispelling function of Saliviae Miltiorrhizae Radix and Notoginseng Radix can significantly reduce the pain of PRS.
Otherwise in hematologic tests, we evaluated the items of WBC, RBC, Hb, Hct, Platelet, PT(INR), aPTT, AST, ALT, BUN and creatinine. In the results, all items were within normal limits. In each group there were no significant changes or abnormal signs between first day and 8 weeks later by multiple comparison. These results means that the therapy of Pletaal with CP is safe in the point of hematology. Bleeding is the major and serious problem of anticoagulant agents, so the evidences of safety on platelet, PT(INR), aPTT are remarkable.
Conclusion
From this study, the therapy of Pletaal with CP is effective to relieve PRS specially in pain and safe on hematologic tests.
Therefore it can reduce the symptoms of PRS and improve the quality of patient’s life. But this study has the limitation of pilot study by small group, so we need to do further and more trials. I think that this study will be helpful for the patients of PRS.