Effects of Kyejiinsam-tang in MIA-Induced Osteoarthritis Rats
Article information
Abstract
Objectives:
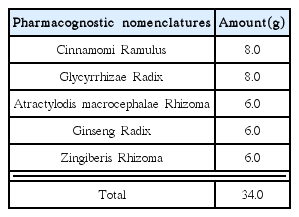
This study investigated the anti-osteoarthritic effects of Kyejiinsam-tang (hereinafter referred to KIT) on the monosodium iodoacetate (MIA)-induced osteoarthritis rats.
Methods:
<in vitro>
Anti-oxidative effects of KIT were measured by scavenging activities of DPPH, reactive oxygen species (ROS) and nitric oxide (NO). Scavenging activities of anti-oxidation in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-treated RAW 264.7 cells were also measured for inhibitory effects against the production of inflammatory mediators (tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-1β, interleukin-6).
<in vivo>
Osteoarthritis was induced in rats by injecting MIA in the knee joint. Rats were divided into a total of 4 groups (n=6). The normal group were not treated at all without inducing osteoarthritis whereas the control group were induced for osteoarthritis by MIA and oral medicated physiological saline per day. The positive comparison group was injected with MIA and after 7 days, 2 mg/kg of Indomethacin. The experimental group was injected with MIA and after 7 days was medicated with 34 mg/kg of KIT. Indomethacin and KIT were orally-medicated for each substance a total of 4 weeks, once per day.
Weight-bearing on hind legs was measured every week after MIA injection. At the end of the experiment (5 weeks after MIA injection), micro CT (computed tomography)-arthrography and histopathological examinations on the articular structures of knee joint were performed. The effect on inflammatory cytokines and immunological cells in synovial fluid was measured. Volume of cartilage was measured by micro CT-arthrography. Injury to synovial tissue was measured by H & E (hematoxylin and eosin), Safranin-O immunofluorescence.
Results:
Cytotoxicity against hFCs was insignificant.
KIT showed the potent full term for DPPH.
<in vitro>
-
NO was significantly reduced by KIT (at 100, 200 μg/ml) and ROS was also reduced, but not significantly, by KIT (at 200 μg/ml).
IL-6 and IL-1β were significantly reduced by KIT (at 100, 200 μg/ml) and TNF-α was also reduced, but not significantly, by KIT (at 200 μ/ml).
<in vivo>
In hind legs weight-bearing measurement, level of weight increased.
Functions of liver and kidney were not affected.
IL-1β was significantly reduced and TNF-α, IL-6 were also reduced but not significantly.
PGE2 (prostaglandin E2), LTB4 (leukotriene B4) were significantly reduced in the KIT group.
MMP-9 (matrix metalloproteinase-9), TIMP-1 (tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1) and Osteocalcin were significantly reduced in the KIT group.
Destruction of cartilage on micro CT arthrography was reduced but had no significant differences.
Histopathologically, injury to synovial membrane of the KIT group was decreased and proteoglycan content of KIT group was increased.
Conclusions:
According to this study, Kyejiinsam-tang has inhibiting effect on the progression of arthritis in MIA-induced osteoarthritis rat. Kyejiinsam-tang has anti-oxidants and anti-inflammation effects, and is related to inhibiting the activity of inflammatory cytokine and injury of volume in cartilage.
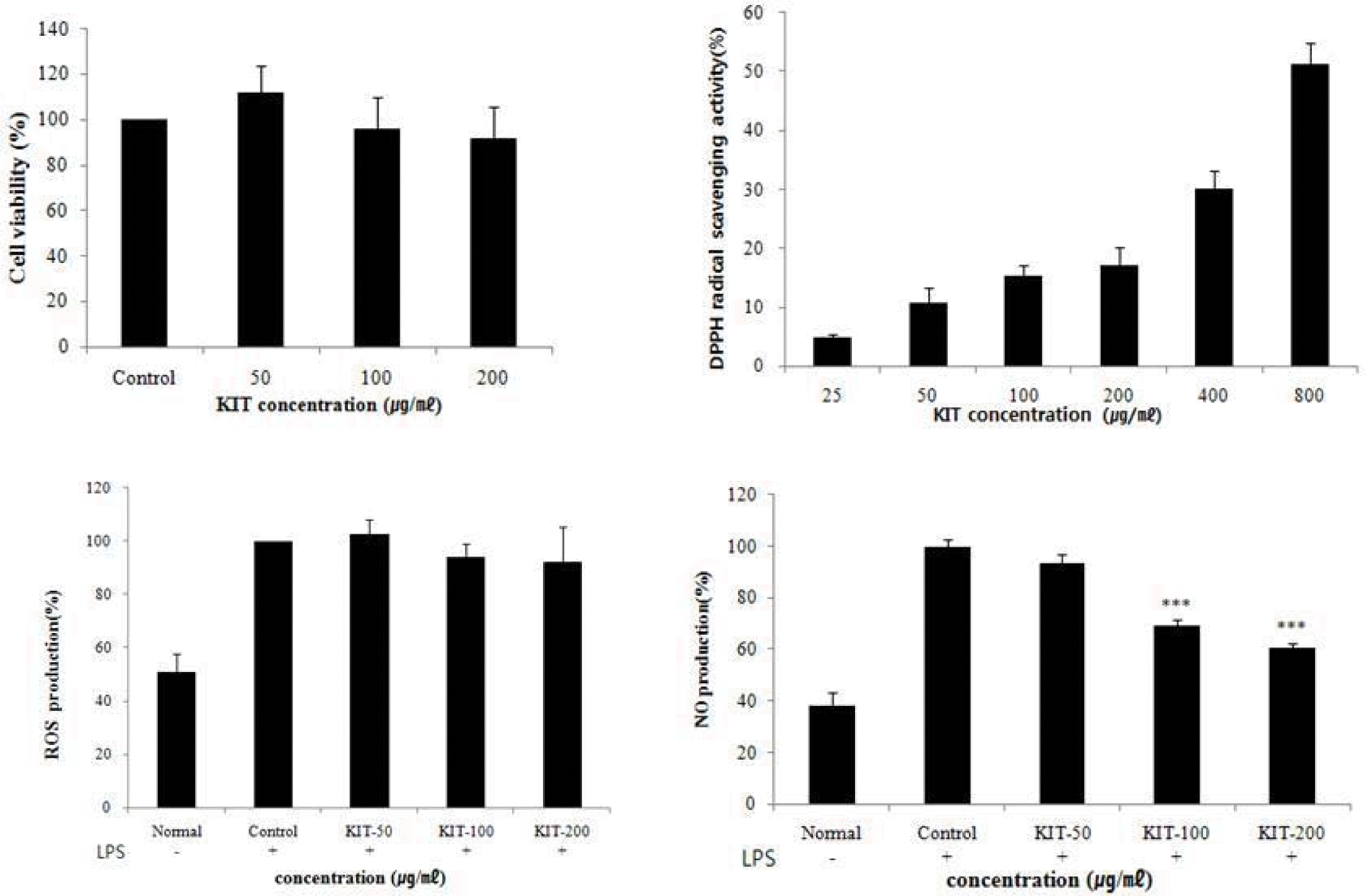
Effects of KIT on the cell viability, DPPH free radical scavenging activity, the Reactive oxygen species(ROS), the Nitric Oxide(NO) of RAW 264.7 cells.
RAW 264.7 cells were treated with 50, 100, 200 μg/ml of KIT for 24 hours. Cell viability was determined using the WST assay. Extracts were incubated with DPPH solution at 37°C for 30 mins. Activities were determined by measurement of absorbance at 517 nm. The ROS production was analysed following incubation with DCFH-DA by flow cytometry. Significant value was calculated by compared with control group by student’s t-test(***p<0.001).
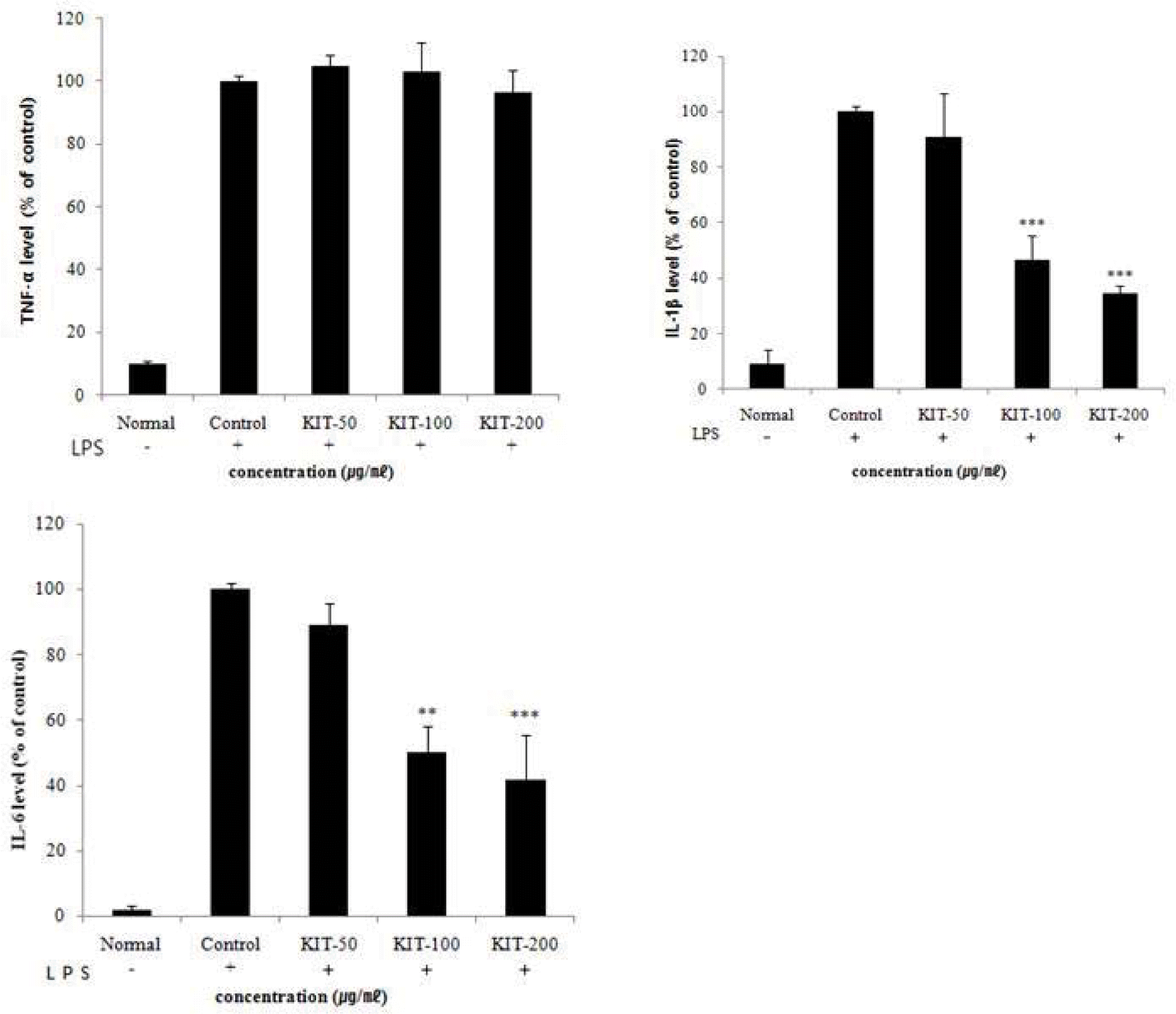
Effects of KIT on LPS-stimulated TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 production in RAW 264.7 cells.
TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-α, IL-1β: interleukin-1β, IL-6: interleukin-6. Cells were treated with LPS(1 μg/ml) and control(0 μg/ml), 50, 100, 200 μg/ml of KIT for 24 hours. The results are expressed as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. Significant value was calculated by compared with control group by student’s t-test(**p<0.01, ***p<0.001).
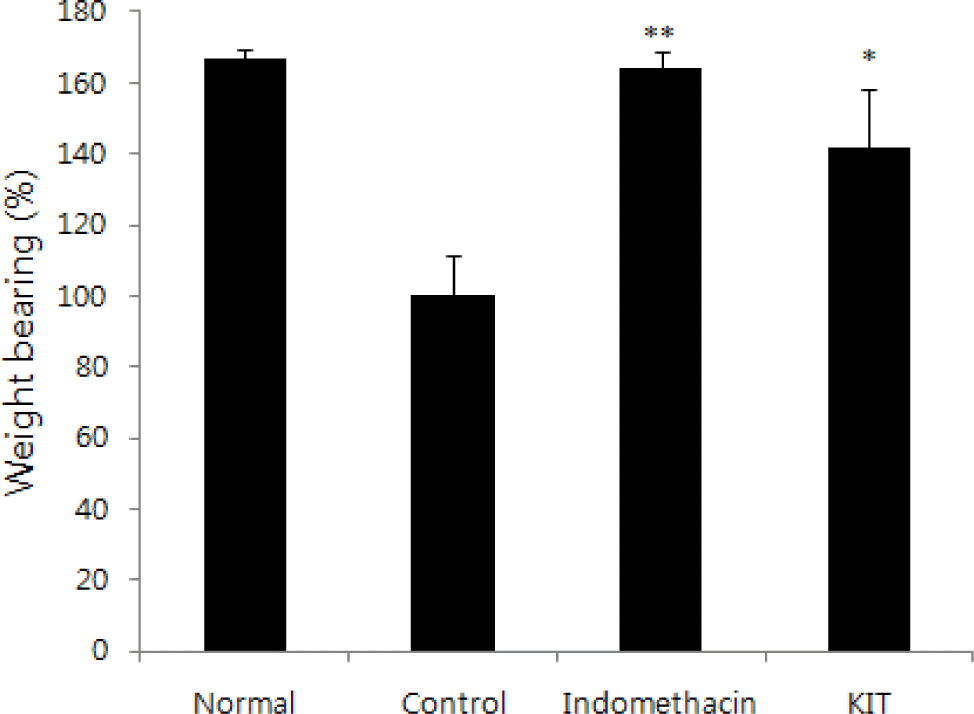
Effects of KIT on weight bearing changes in the hind legs of MIA-induced osteoarthritis rats.
Normal; Normal Wister rat group, Control; MIA-induced osteoarthritis group treated with normal saline, Indomethacin; MIA-induced osteoarthritis group treated with Indomethacin, KIT; MIA-induced osteoarthritis group treated with KIT. The results are expressed as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. Statistically significant value compared with control by t-test(*p<0.05, **p<0.01).
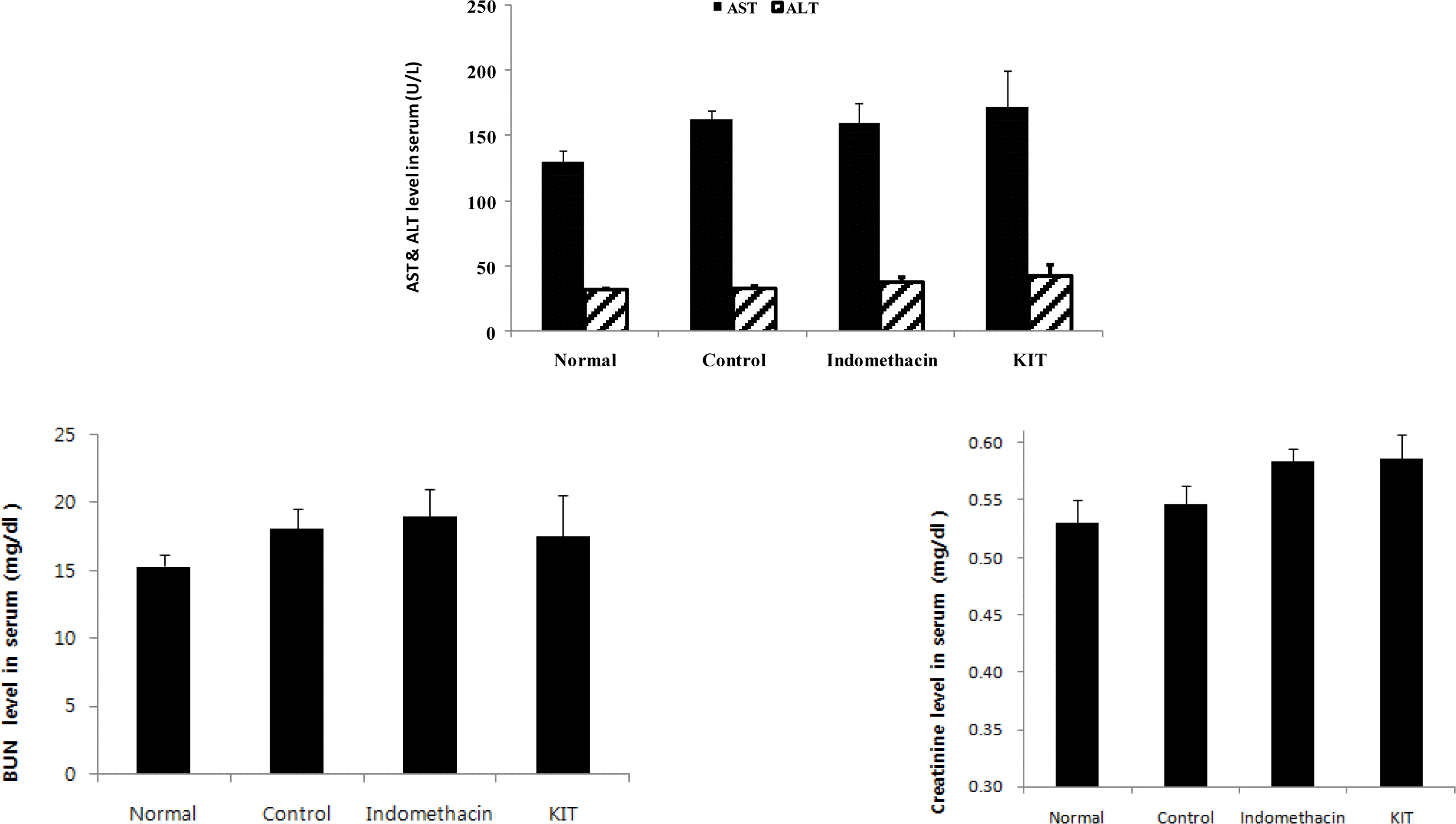
Effect of KIT on the AST and ALT, BUN and creatinine in MIA-induced osteoarthritis rats.
Normal; Normal Wister rat group, Control; MIA-induced osteoarthritis group treated with normal saline, Indomethacin; MIA-induced osteoarthritis group treated with Indomethacin, KIT; MIA-induced osteoarthritis group treated with KIT. AST: aspatrate aminotransferase, ALT: alanine aminotransterase, BUN: blood urea nitrogen. Values represent the means ± SD.
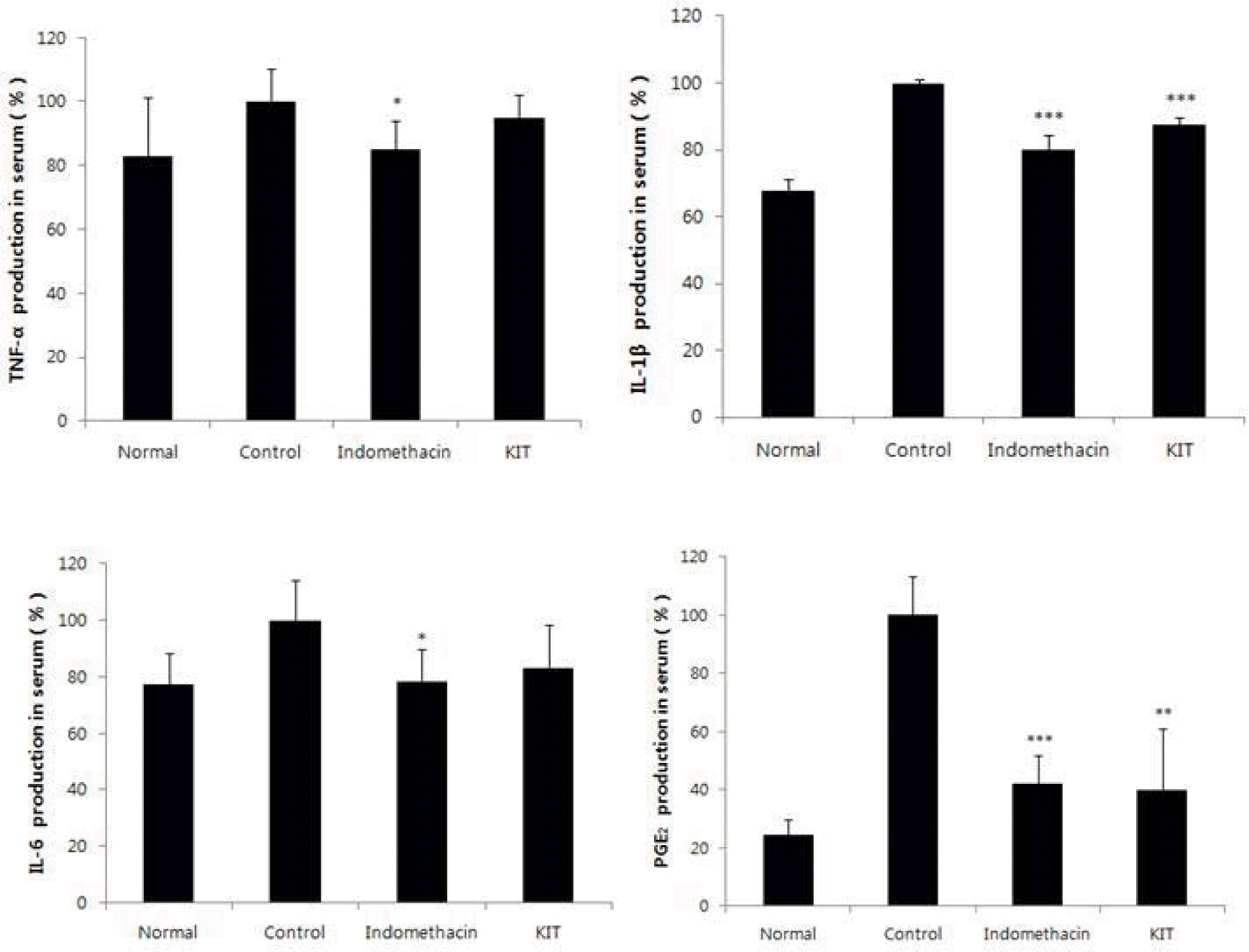
Effects of KIT on levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, PGE2 in the serum of MIA-induced osteoarthritis rats.
Normal; Normal Wister rat group, Control; MIA-induced osteoarthritis group treated with normal saline, Indomethacin; MIA-induced osteoarthritis group treated with Indomethacin, KIT; MIA-induced osteoarthritis group treated with KIT, TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-α, IL-1β: interleukin - 1β, IL-6: interleukin-6, PGE2: Prostaglandin E2. Values represent the means ± SD. Statistically significant value compared with control by t-test(*p<0.05, ** p<0.01, ***p<0.001).
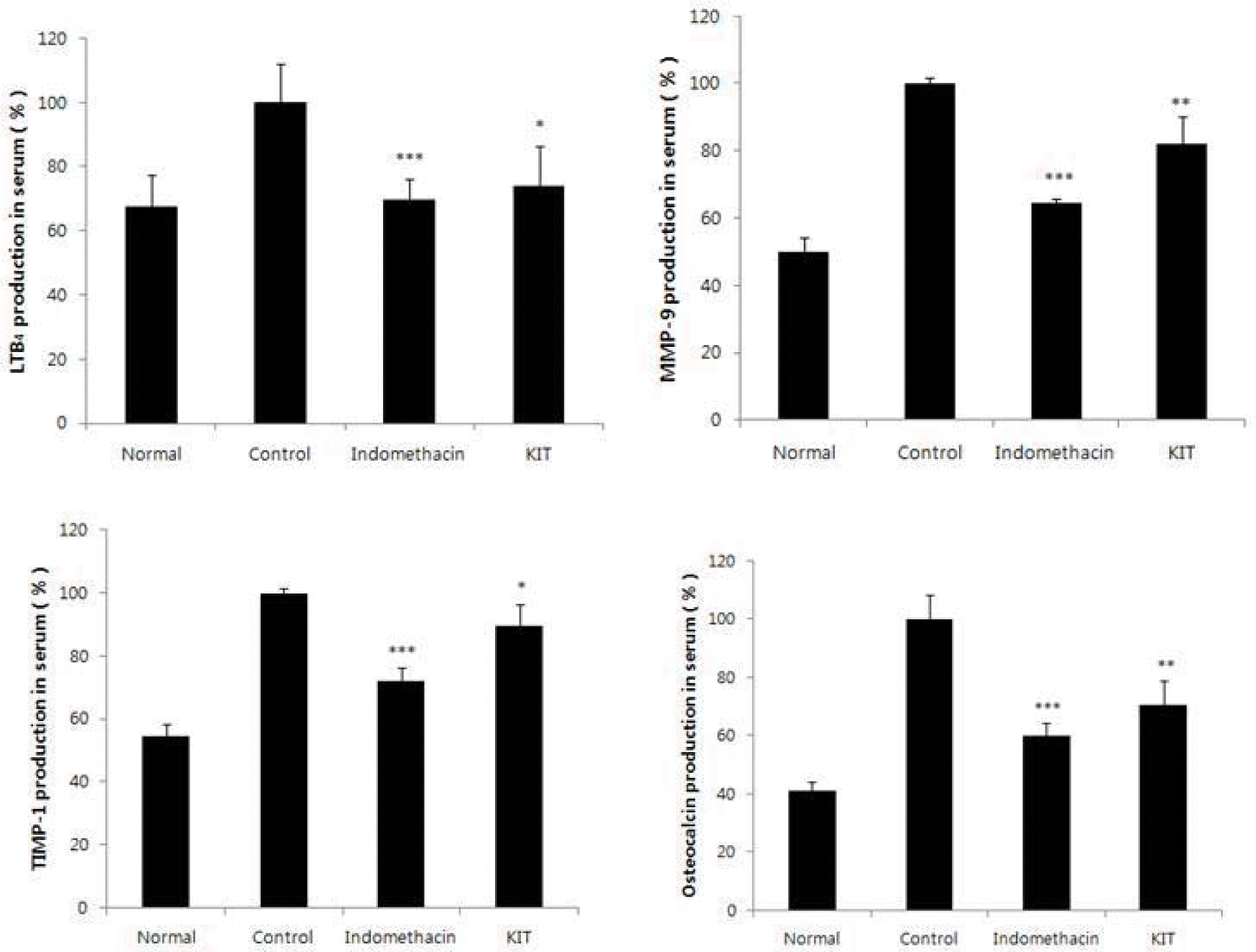
Effects of KIT on levels of LTB4, MMP-9, TIMP-1, Osteocalcin in the serum of MIA-induced osteoarthritis rats.
Normal; Normal Wister rat group, Control; MIA-induced osteoarthritis group treated with normal saline, Indomethacin; MIA-induced osteoarthritis group treated with Indomethacin, KIT; MIA-induced osteoarthritis group treated with KIT, LTB4: Leukotriene B4, MMP-9: Matrix metalloproteinase-9, TIMP-1: Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1. Values represent the means ± SD. Statistically significant value compared with control by t-test(*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001).
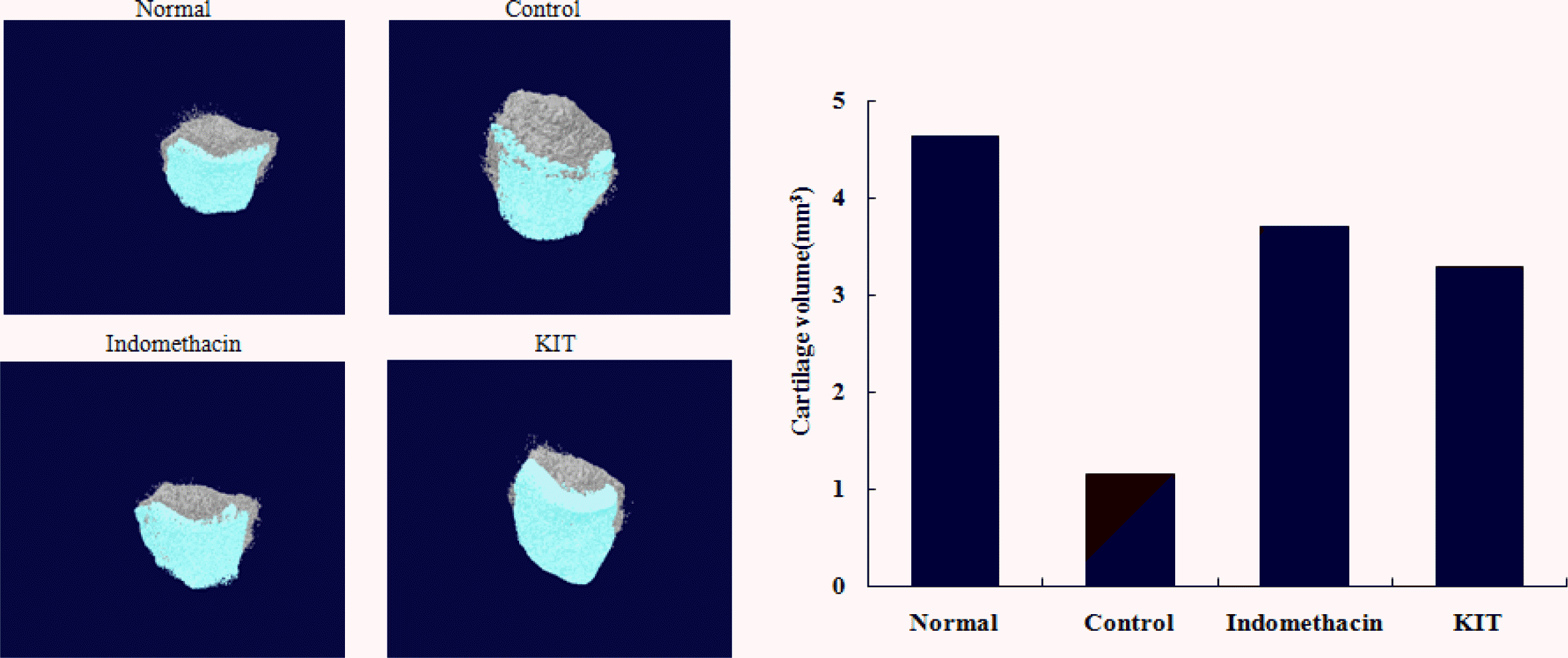
Effects of KIT on imaging and volume of cartilage degeneration using micro CT arthrography in joint tissue of MIA-induced osteoarthritis rats.
Normal; Normal Wister rat group, Control; MIA-induced osteoarthritis group treated with normal saline, Indomethacin; MIA-induced osteoarthritis group treated with Indomethacin
KIT; MIA-induced osteoarthritis group treated with KIT
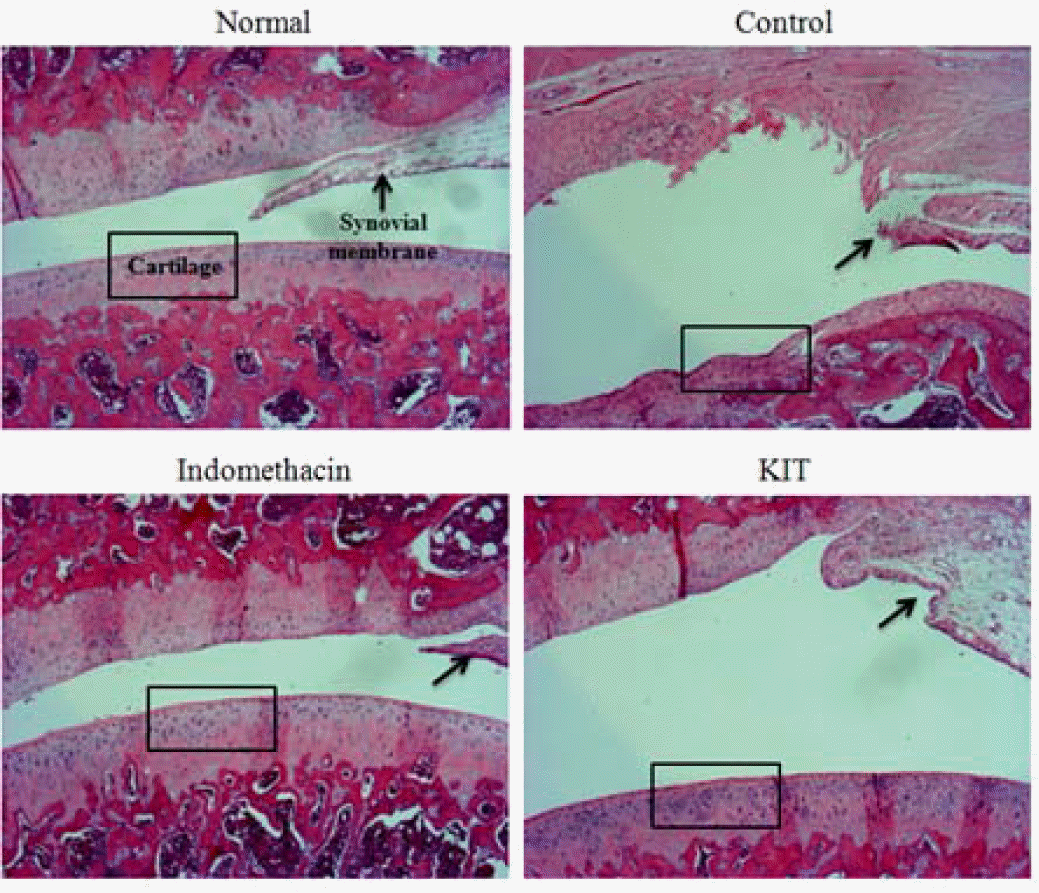
Effects of KIT on joint pathology(hematoxylin & eosin staining) from joint tissue of MIA-induced osteoarthritis rats(× 100).
Normal; Normal Wister rat group, Control; MIA-induced osteoarthritis group treated with normal saline, Indomethacin; MIA-induced osteoarthritis group treated with Indomethacin, KIT; MIA-induced osteoarthritis group treated with KIT. In normal, articular cartilages are sell developed. In control, most of articular cartilage was degenerated. In Indomethacin and KIT, most of articular cartilages are degenerated and appeared homogeneous, but proteoglycan in periphery of degenerated area are remained.
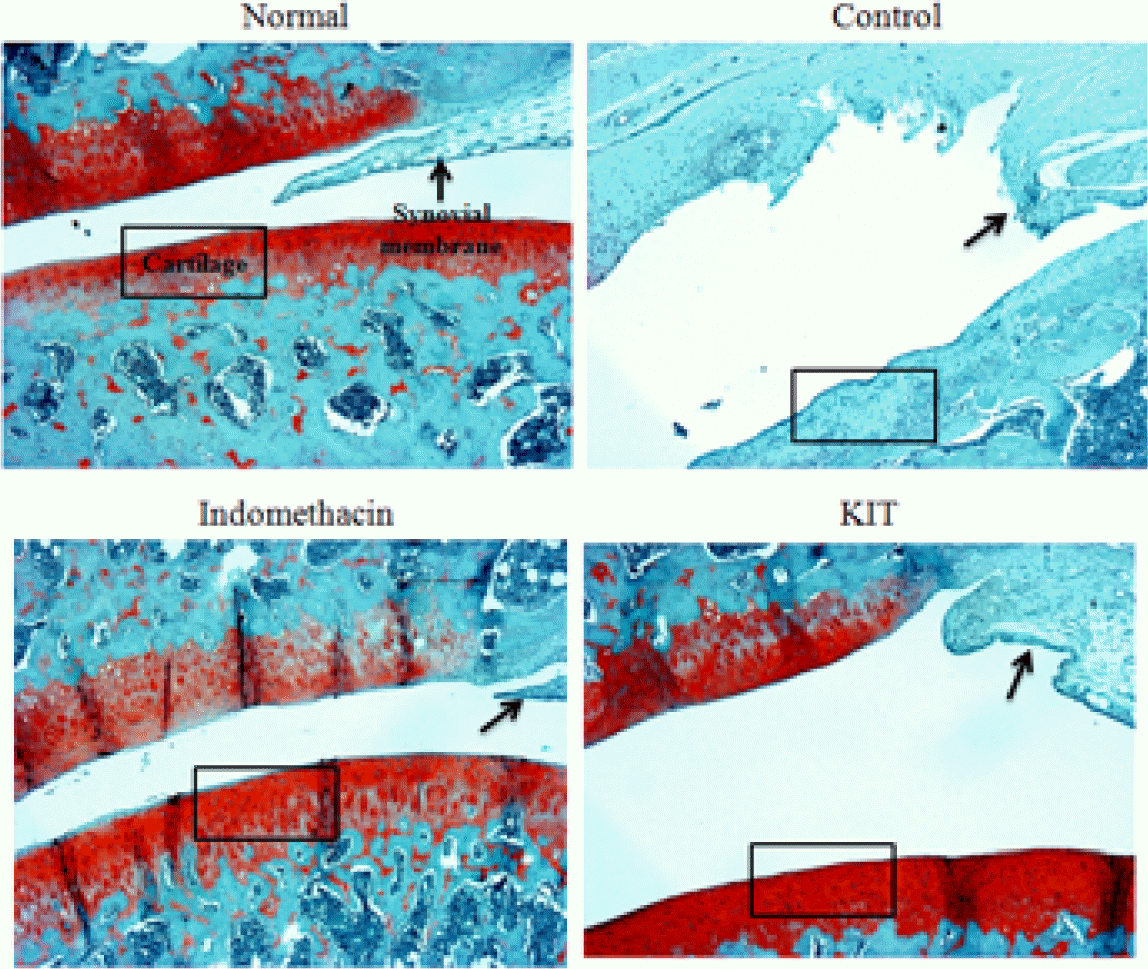
Effects of KIT on joint pathology(Safranin-O staining) from joint tissue of MIA-induced osteoarthritis rats(× 100).
Normal; Normal Wister rat group, Control; MIA-induced osteoarthritis group treated with normal saline, Indomethacin; MIA-induced osteoarthritis group treated with Indomethacin, KIT; MIA-induced osteoarthritis group treated with KIT. Stain intensity of red color increased in proportion to proteoglycan content in normal. The red color disappeared in almost articular cartilage and red color remained in periphery of necrotic area in control. Compare the stain intensity and areas of red color in Indomethacin and KIT with the normal and control.