References
1. De Seta D, Mancini P, Minni A, Prosperini L, De Seta E, Attanasio G, et al. Bell’s palsy: symptoms preceding and accompanying the facial paresis. Scientific World Journal 2014;Article ID 801971.
2. holland NJ, Weiner GM. Recent developments in Bell’s palsy. The British Medical Journal 2004;329:553–7.
5. Hong CK, Byun JY, Yeo SG, Park MS, Cha CI. Usefulness of Botulinum Toxin Injection in Rehabilitation of Facial Paralysis: Improving Mouth Angle Asymmetry. Korean J Otorhinolaryngol -Head Neck Surg 2007;50:1087–91.
6. Lee WS, Kim J. Facial Nerve Paralysis and Surgical Management. J Korean Med Assoc 2009;52(8):807–818.
7. Hong KE. Prevalence and Treatment Pattern of Korean Patients with Facial Palsy. The Journal of Korean Acupuncture & Moxibustion Society 2010;27(3):137–146.
9. Fu L, Bundy C, Sadiq SA. Psychological distress in people with disfigurement from facial palsy. Eye 2011;25:1322–6.
10. Anderson G. Anxiety, optimism, and symptoms reporting following surgery for acoustic neuroma. J Psychosom Res 1999;46(3):257–60.
11. Van Swearingen JM, Cohn J, Turnbull J, Mirzai T, Johnson P. Psychological distress: linking impairment with disability in facial neuromotor disorders. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1998;118(6):790–6.
12. Peitersen E. Bell’s palsy : the spontaneous course of 2,500 peripheral facial nerve palsies of different etiologies. Acta Otolaryngol 2002;Suppl 549. 122:4–30.
13. Kim JI, Seo JC, Lee SH, Choi DY, Kang SK, Koh HK. The clinical observation on Bell’s palsy according to facial nerve grading system. The Journal of Korea Acupuncture & Moxibustion Society 2002;19(5):112–123.
14. Gronseth GS, Paduga R. Evidence-based guideline update: steroids and antivirals for Bell palsy: report of the Guideline Development Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2012;79(22):2209–13.
15. Yi YJ, Kim HJ, Ryu EK. Comparison of Efficacy between Acupuncture Treatment and Collaborative Treatment with Prednisolone on Acute Bell’s Palsy. Journal of Korean Medicine Rehabilitation 2013;23(3):125–132.
16. Chu MG, Jo HG, Choi JB, Kim SJ, Park KM, Cho GR, et al. ing Facial Acupuncture. Korean J Oriental Physiology & Pathology 2009;23(5):1188–1192.
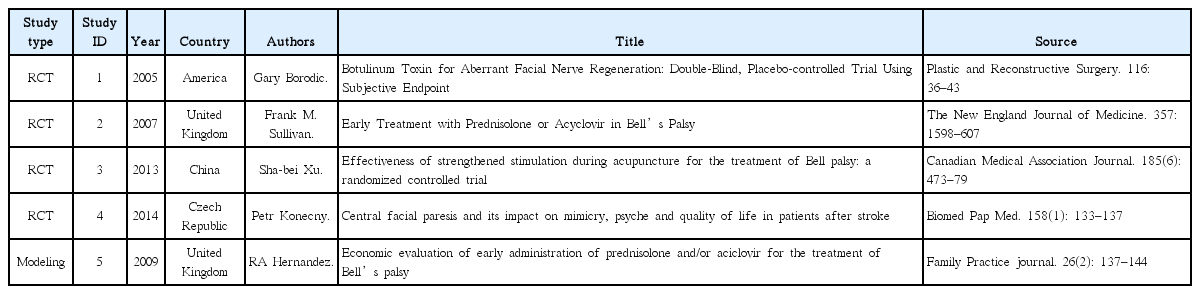
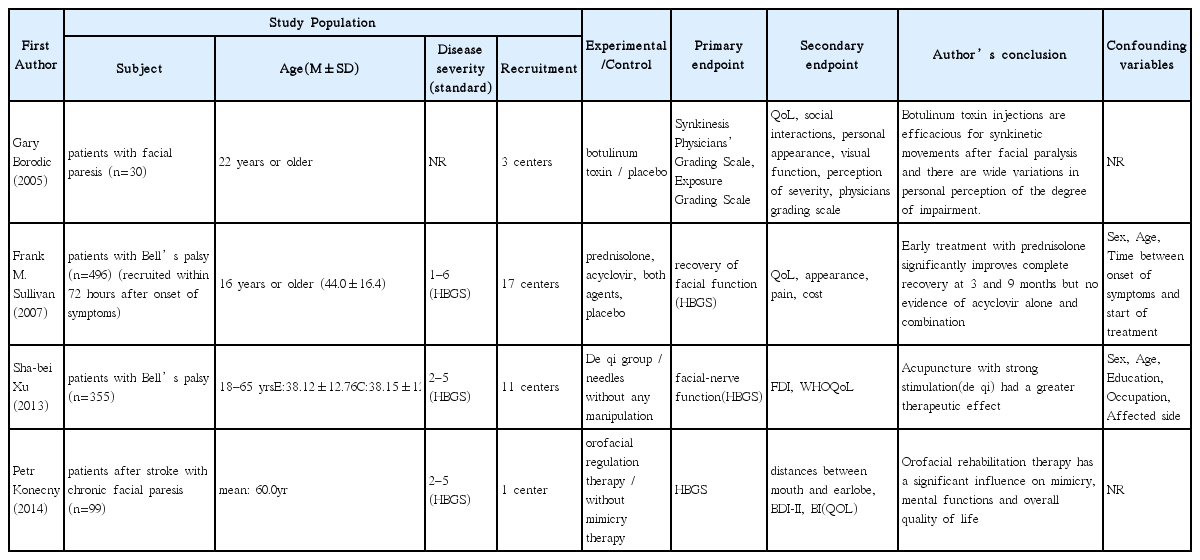
17. Borodic G, Bartley M, Slattery W, Glasscock M, Johnson E, Malazio C, et al. Botulinum Toxin for Aberrant Facial Nerve Regeneration: Double-Blind, Placebo -controlled Trial Using Subjective Endpoint. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 2005;116:36–43.
18. Sullivan FM, Iain RCS, Donnan PT. Early Treatment with Prednisolone or Acyclovir in Bell’s Palsy. The New England Journal of Medicine 2007;357:1598–607.
19. Xu SB, Huang B, Zhang CY, Du P, Yuan Q, Bi GJ, Xie MJ, et al. Effectiveness of strengthened stimulation during acupuncture for the treatment of Bell palsy: a randomized controlled trial. Canadian Medical Association Journal 2013;185(6):473–79.
20. Konecny P, Elfmark M, Horak S, Pastucha D, Krobot A, Urbanek K, et al. Central facial paresis and its impact on mimicry, psyche and quality of life in patients after stroke. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub 2014;158(1):133–137.
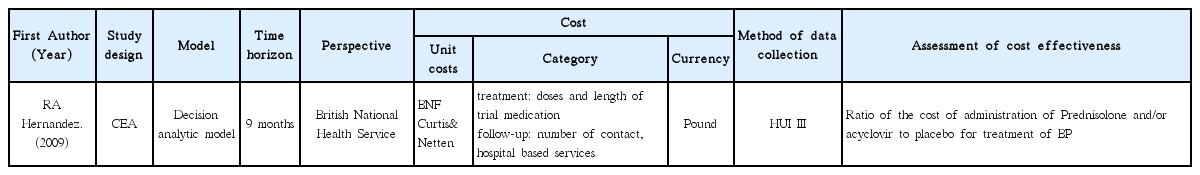
21. Hernandez RA, Sullivan F, Donnan P, Swan I, Vale L. Economic evaluation of early administration of prednisolone and/or aciclovir for the treatment of Bell’s palsy. Family Practice journal 2009;26(2):137–144.