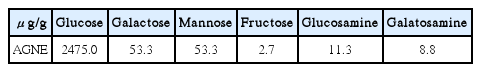
The Effect of Angelica gigas Nakai Extract and Bacillus Polyfermenticus KJS-2 on Atopic Dermatitis induced by DNCB in mice
Article information
Abstract
Objectives
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of Angelica gigas Nakai extract(AGNE) and Bacillus polyfermenticus KJS-2 (BP2) on atopic dermatitis (AD) induced by 2, 4-dinitrochlorobenzene (DNCB) in mice.
Methods
In the experiment, we divided mice into four groups: a control group, a DNCB group, an AGNE group, and an AGNE+BP2 group. Then we examined the changes in scratching frequency, clinical aspects on dorsum skin, immunoglobulin (IgE), cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6) and expression of COX-2.
Resutls
From the experiment, the scratching frequency was significantly dropped in AGNE group and AGNE+BP2 group. Clinical observations of dorsum skin, there were a severe keratotic lesion and drop of dead skin cell in DNCB group, but symptoms of AD were decreased 39.6% in AGNE group and 49.6% in AGNE+BP2 group during 3 weeks. IgE, TNF-α and IL-6 were decreased significantly in both AGNE and AGNE+BP2 group. Expression of COX-2 was also decreased significantly in both groups.
Conclusions
In conclusion, these data suggest that AGNE can decrease symptoms of AD and BP2 makes AGNE more effective. So AGNE can be useful herbal therapy for AD.
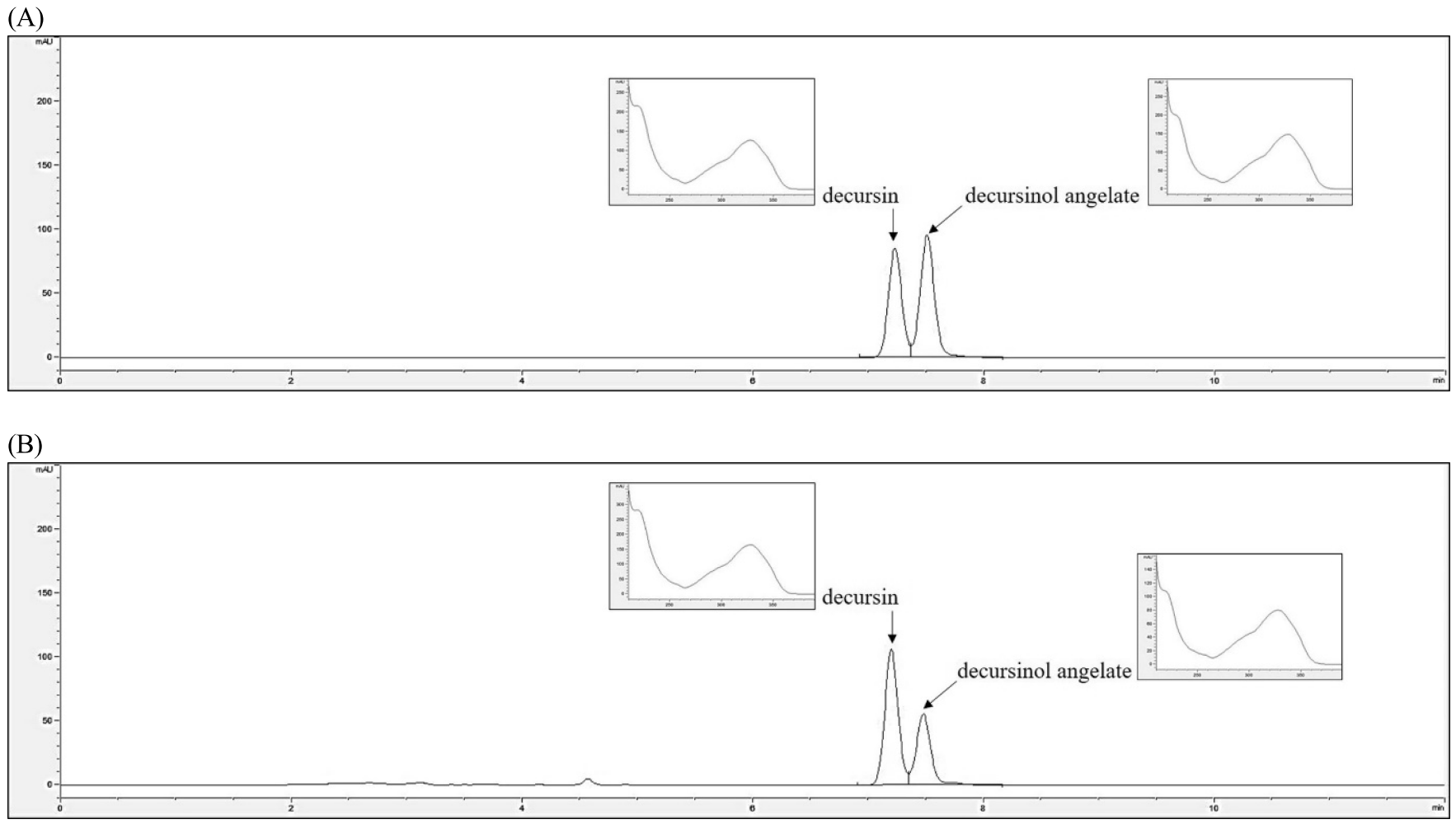
Representative high-performance liquid chromatography profile (A) Decursin and decursinol angelate of standard materials (B) AGNE sample.
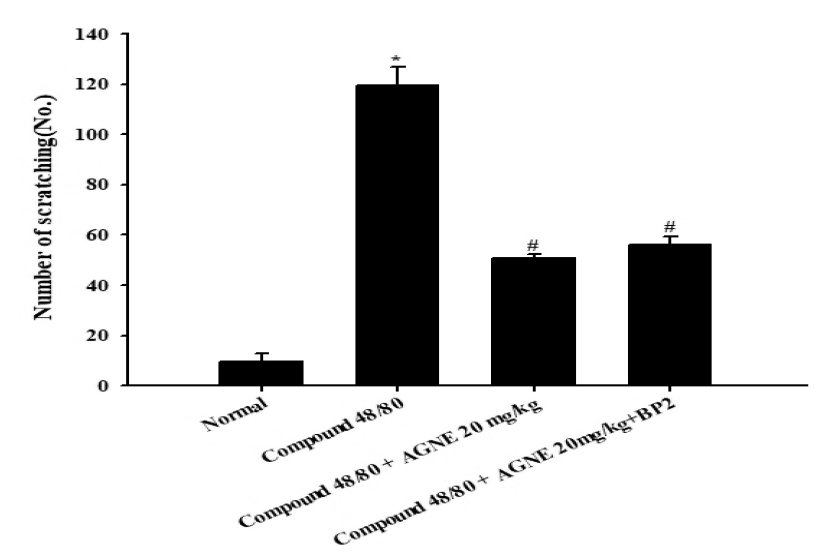
The effect of AGNE and AGNE+BP2 on scratching behavior induced by compound 48/80 in ICR mice. AGNE(20 mg/kg), AGNE(20 mg/kg)+BP2(107 CFU) administered orally on the scratching behavior induced by compound 48/80 (50 μg/mouse, s.c.) in mice. AGNE and AGNE+BP2 significantly inhibited the compound 48/80-induced scratching behavior than DNCB group. Each datum represents the means ± S.E.M. of three independent experiments. (*p<0.05 vs. normal group, #p<0.05 vs. compound 48/80-treated group).
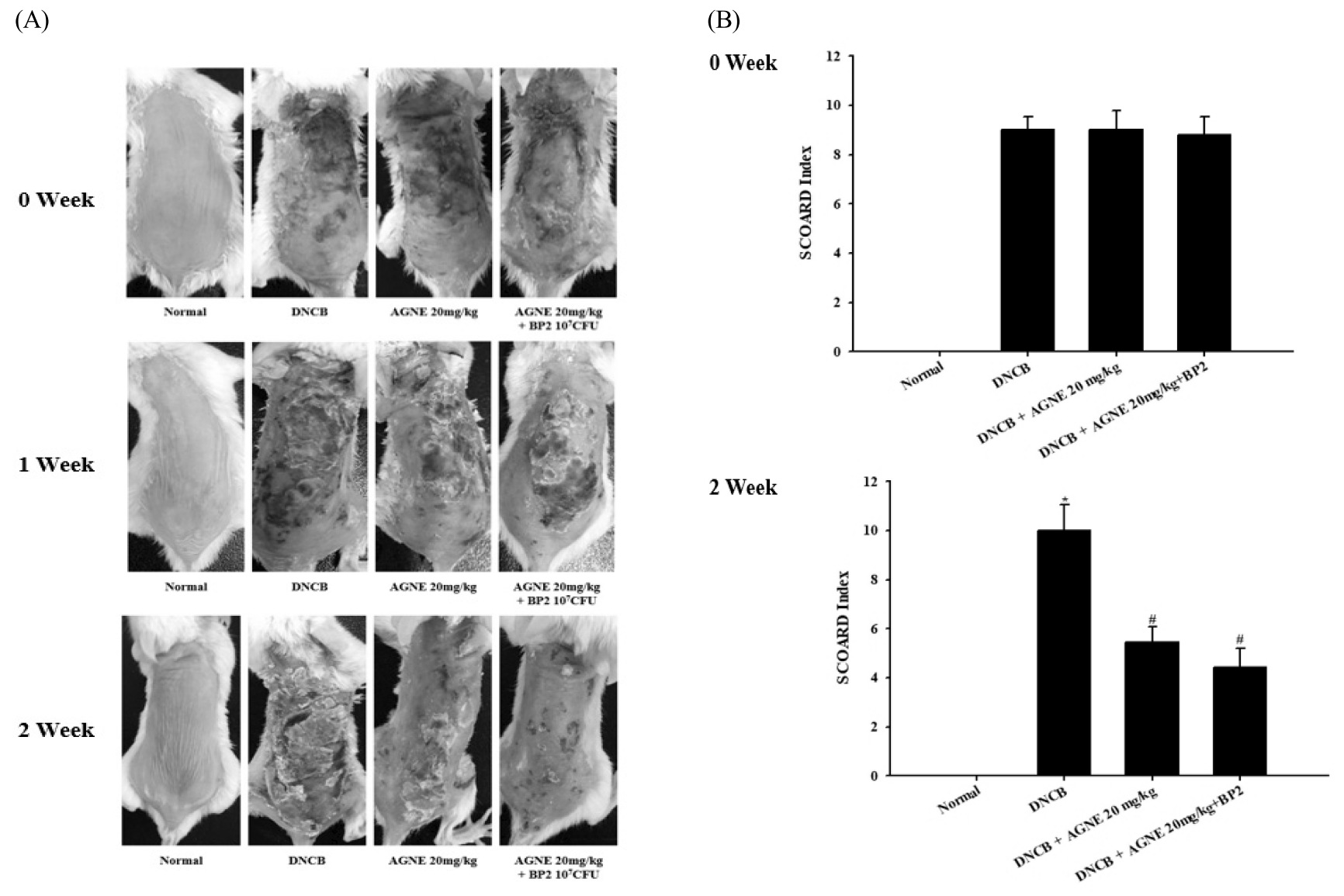
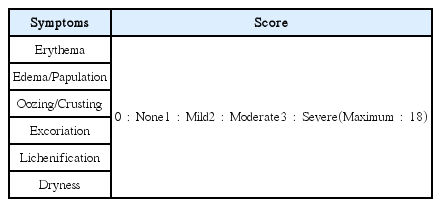
The effect of AGNE and AGNE+BP2 on the DNCB-induced atopic dermatitis. The BALB/c mice (n=6) were sensitized with 150 μL of 0.5% DNCB in acetone–olive oil(3:1) or vehicle applied to the dorsal skin twice each week for a total period of 3 weeks. After 2 weeks, AGNE(20 mg/kg) and AGNE(20 mg/kg)+BP2(107 CFU) was orally administered 1 week prior to the end of the experiment. (A) Comparison of skin manifestation in all groups for 3 weeks (B) SCORAD index of all groups in 0week and 2 weeks. (*p<0.05 vs. normal group, #p<0.05 vs. compound 48/80-treated group).
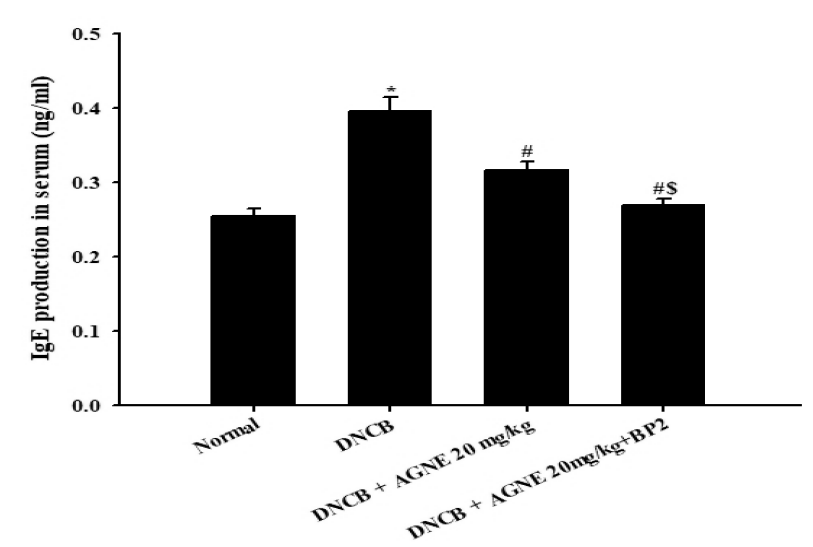
The effect of AGNE and AGNE+BP2 on the DNCB-induced IgE level in serum from mice. Blood samples were collected and then the levels of serum IgE in the indicated groups were measured using ELISA method. AGNE and AGNE+BP2 significantly inhibited the DNCB-induced IgE level in serum. Each datum represents the means ±± S.E.M. of three independent experiments(*p<0.05 vs. normal group, #p<0.05 vs. DNCB-treated group, $p<0.05 vs. DNCB+AGNE 20 mg/kg-treated group).
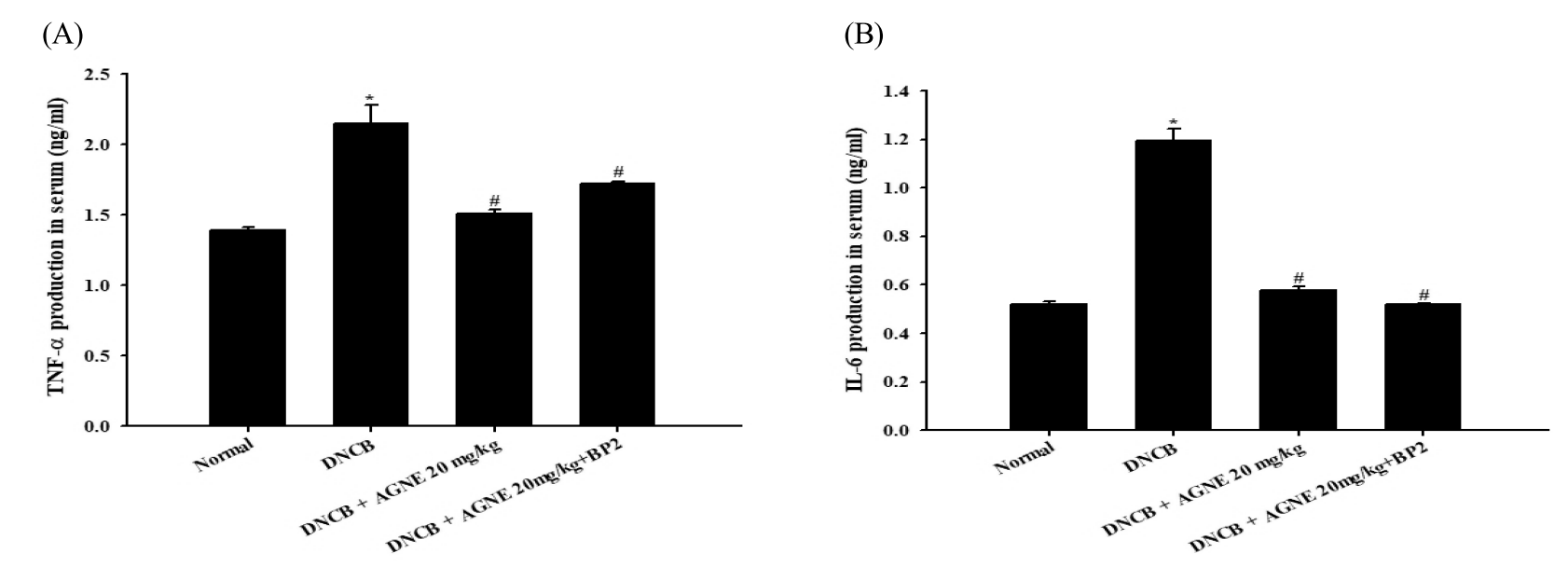
The effect of AGNE and AGNE+BP2 on the DNCB-induced (A) TNF-α and (B) IL-6 levels in serum from mice. Blood samples were collected and then the levels of serum TNF-α and IL-6 in the indicated groups were measured using ELISA method. AGNE+BP2 significantly inhibited the DNCB-induced TNF-α and IL-6 level in serum. Each datum represents the means ± S.E.M. of three independent experiments (*p<0.05 vs. normal group, #p<0.05 vs. DNCB-treated group).
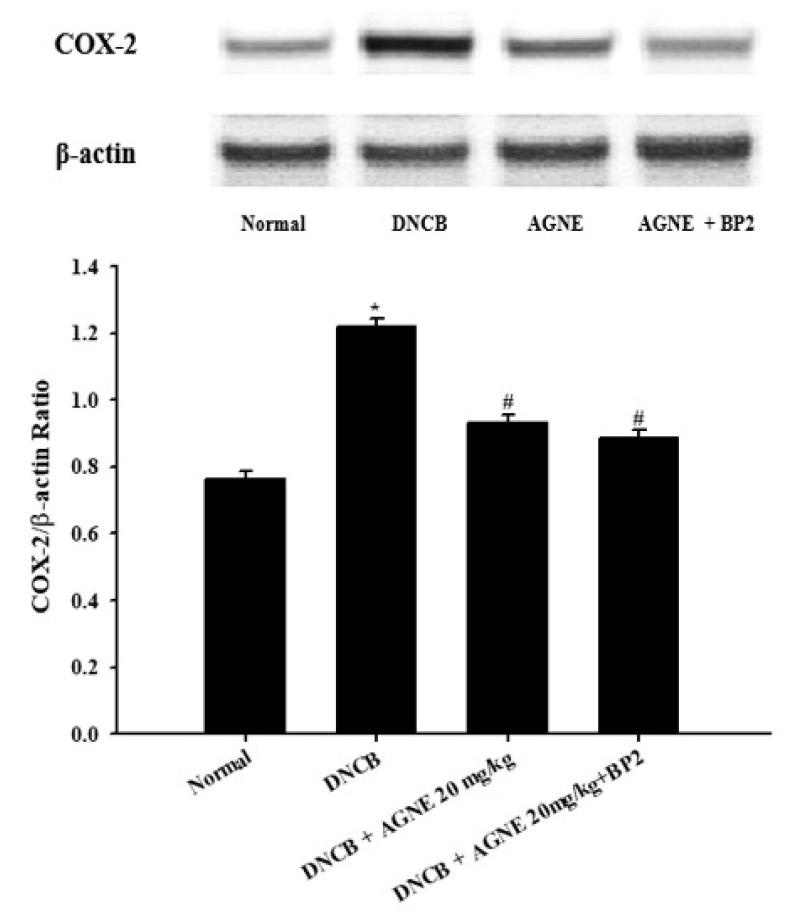
The effect of AGNE and AGNE+BP2 on the DNCB-induced COX-2 levels in tissue from mice. Tissue samples were collected and then the levels of tissue COX-2 protein in the indicated groups were measured using Western blotting method. AGNE+BP2 significantly inhibited the DNCB-induced COX-2 level in tissue. Each datum represents the means ± S.E.M. of three independent experiments (*p<0.05 vs. normal group, #p<0.05 vs. DNCB-treated group).