Inhibition of gene associated with Dyslipidemia and Antioxidative Effect of Artemisia iwayomogi, Curcumae Radix and Raphani Semen(ACR) on HepG2 cell model
Article information
Abstract
Objectives
We performed this study to evaluate the antioxidative and hypolipidemic effect of Artemisia iwayomogi (韓茵蔯), Curcuma longa L. (鬱金) and Raphanus sativus L. (蘿葍子) (ACR).
Method
We enriched Artemisiae Capillaris, Curcumae Longae and Raphani Semen compound with alcohol. ACR extract is treated to HepG2 cell. Cell groups are devided into 3 groups: normal, control and ACR treated group. We measured polyphenol, flavonoids, DPPH and ABTS radical scavenging activity, ROS, glutathione, GSH peroxidase, GSH reductase, SOD, catalase, free fatty acid, lipid peroxidation and suppression of ACAT1 and HMG-CoA reductase expression on mRNA level.
Results
ACR contained polyphenol and flavonoids and increased GSH significantly in HepG2 cell.
ACR increased GPx, GR, and catalase activity significantly in HepG2 cell.
ACR increased DPPH and ABTS radical scavenging activity significantly in HepG2 cell and decreased ROS.
ACR decreased free fatty acid and MDA significantly in HepG2 cell.
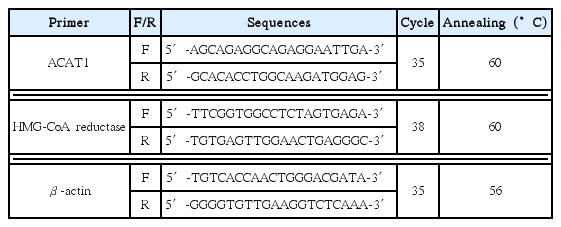
ACR suppressed ACAT1 and HMG-CoA reductase expression on mRNA level in HepG2 cell.
Conclusion
This study suggests that ACR has antioxidative and hypolipidemic effect and might be effective in prevention and treatment of dyslipidemia.
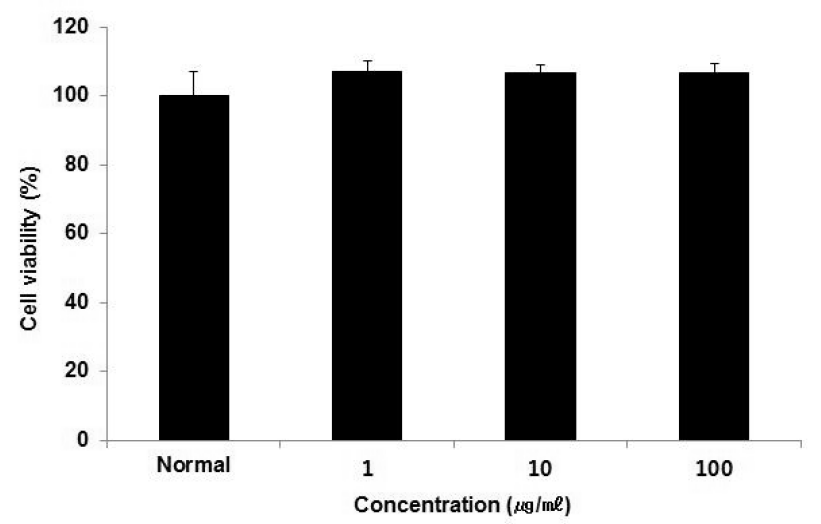
Cell viability of HepG2 cells treated ACR extract.
Cell viability was calculated as percentage versus normal. The result were presented by the mean ± S.D from three independent experiments
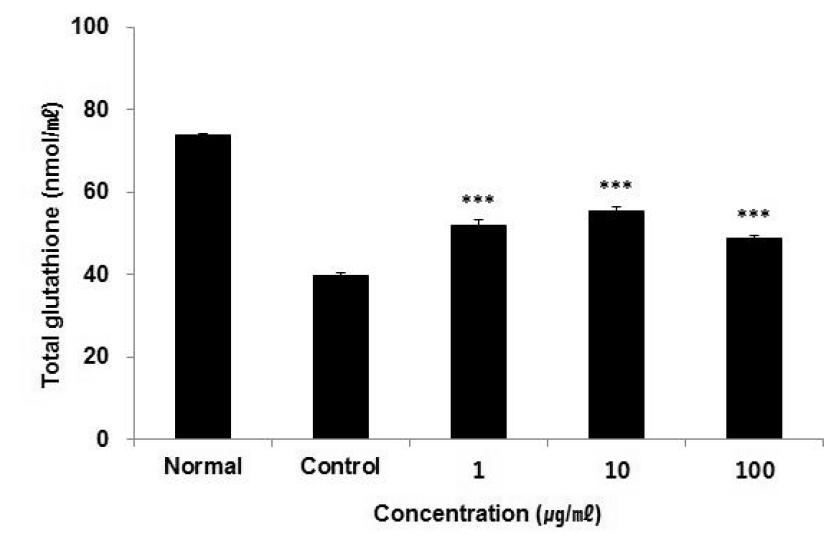
Effect of ACR extract on total GSH contents in HepG2 cells.
Total GSH contents were calculated using GSH standard curve. The result were presented by the mean ± S.D from three independent experiments (Significance of results, ***: p<0.001 compare to control). Normal; non-treated HepG2 cells. Control; 1 mM H2O2-treated HepG2 cells.
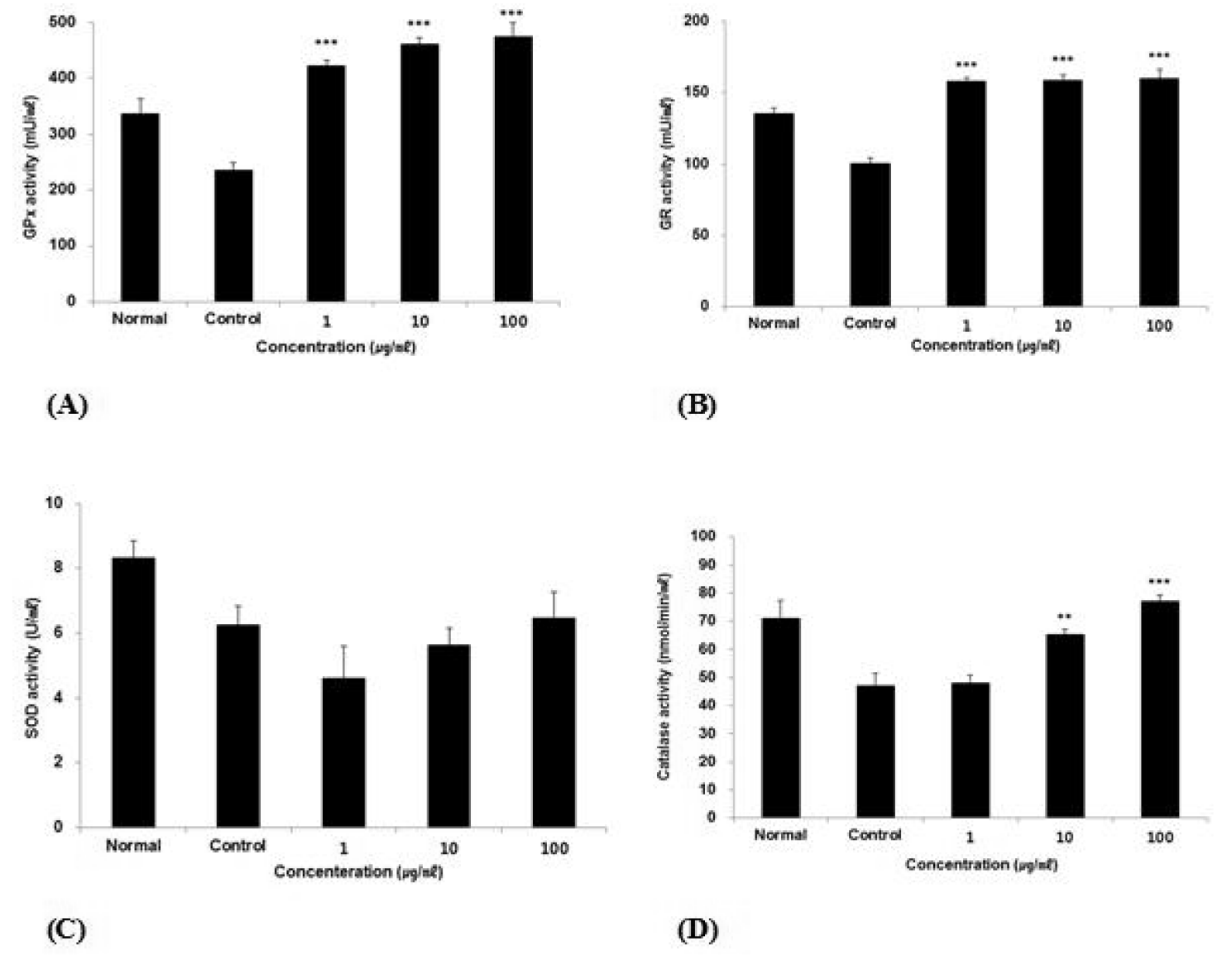
Effect of ACR extract on GPx, GR, SOD and Catalase activity in HepG2 cells.
(A) GPx activity was calculated using NADPH standard curve.
(B) GR activity was calculated using TNB standard curve.
(C) SOD activity was calculated using SOD standard curve.
(D) Catalase activity was calculated using H2O2 standard curve.
The result were presented by the mean ± S.D from three independent experiments (Significance of results, **: p<0.01, ***: p<0.001 compare to control). Normal; non-treated HepG2 cells. Control; 1 mM H2O2-treated HepG2 cells.
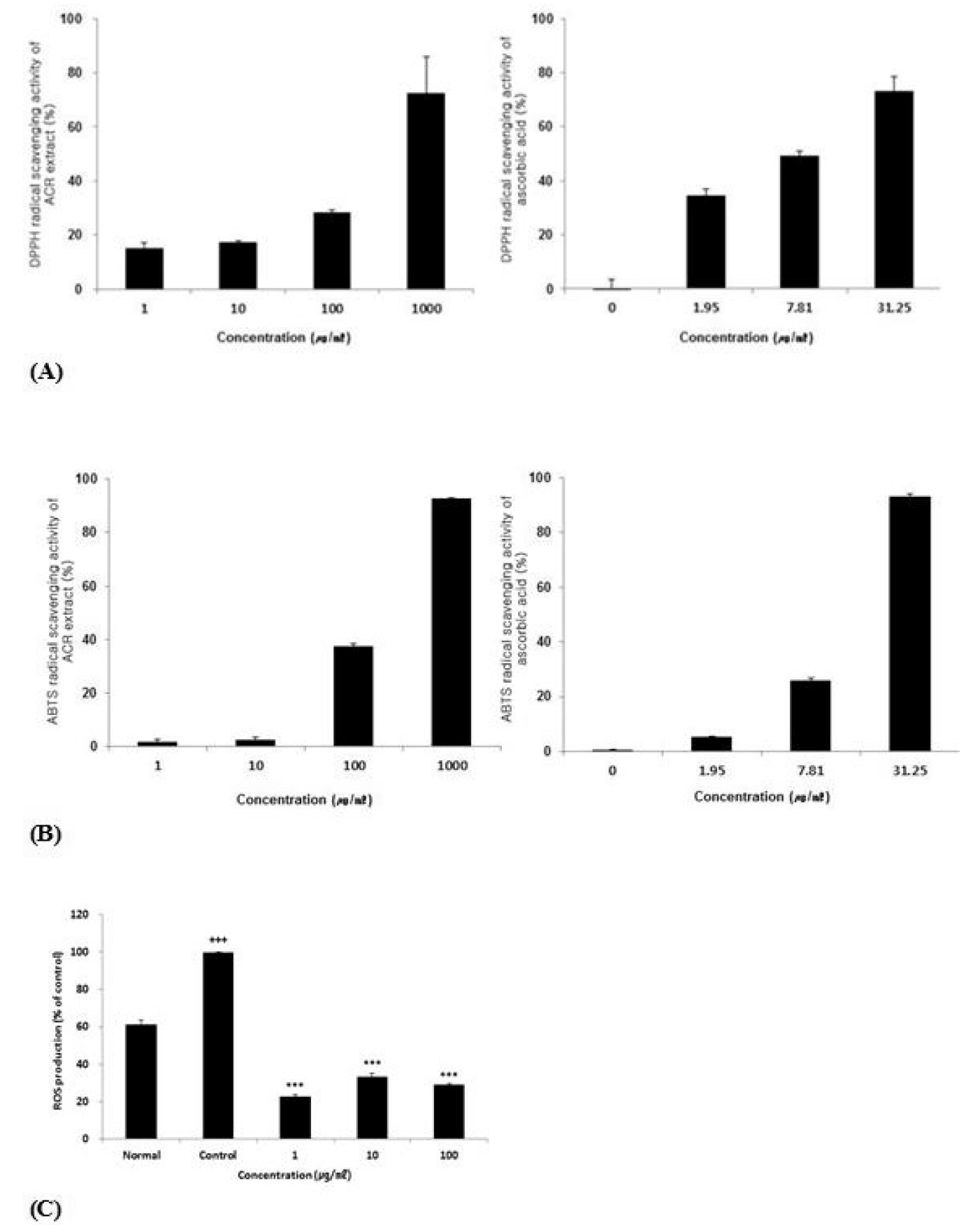
DPPH and ABTS radical scavenging activity of ACR extract and effect of ACR extract on ROS production in HepG2 cells.
(A) DPPH radical scavenging activity of ACR extract comparing to ascorbic acid.
(B) ABTS radical scavenging activity of ACR extract comparing to ascorbic acid.
(C) Effect of ACR extract on ROS production in HepG2 cells. Level of ROS was calculated as percentage versus control. Normal; non-treated HepG2 cells. Control; 1 mM H2O2-treated HepG2 cells.
The result were presented by the mean ± S.D from three independent experiments (Significance of results, ***: p<0.001 compare to control).
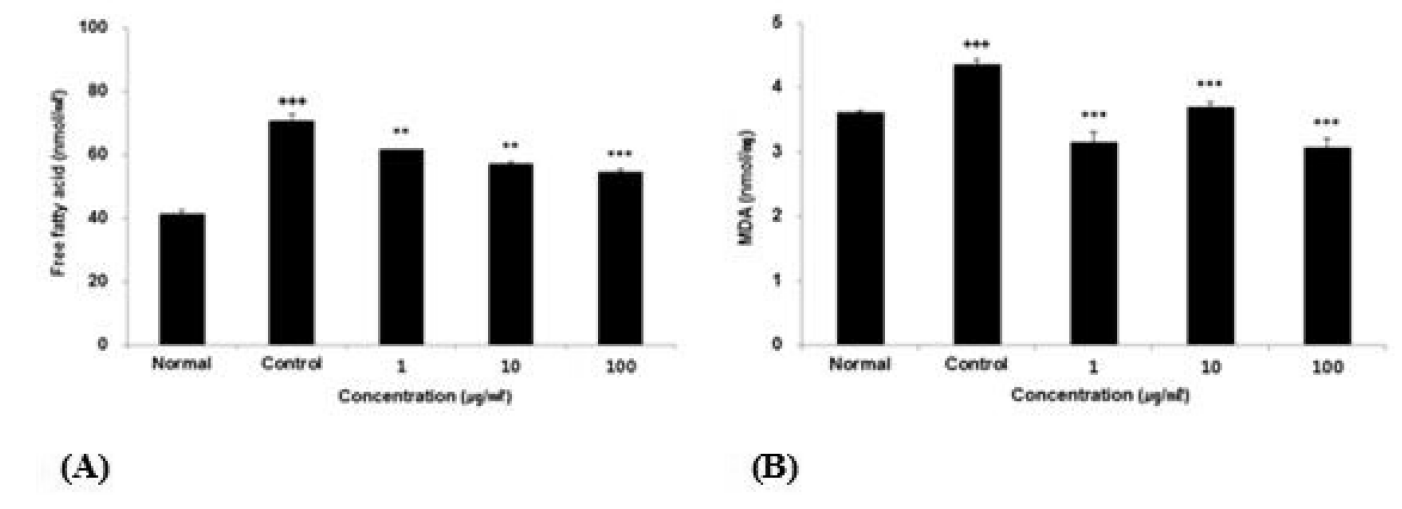
Effect of ACR extract on free fatty acid contents and MDA in HepG2 cells.
(A) Free fatty acid contents were calculated using palmitate standard curve. Normal ; non-treated HepG2 cells, Control ; 0.5 mM FAs (palmitate;oleic acid, 6:4)-treated HepG2 cells.
(B) Lipid peroxidation (MDA) was calculated using MDA standard curve. Normal ; non-treated HepG2 cells, Control ; 1 mM H2O2-treated HepG2 cells.
The result were presented by the mean ± S.D from three independent experiments (Significance of results, **: p<0.01, ***: p<0.001 compare to control).
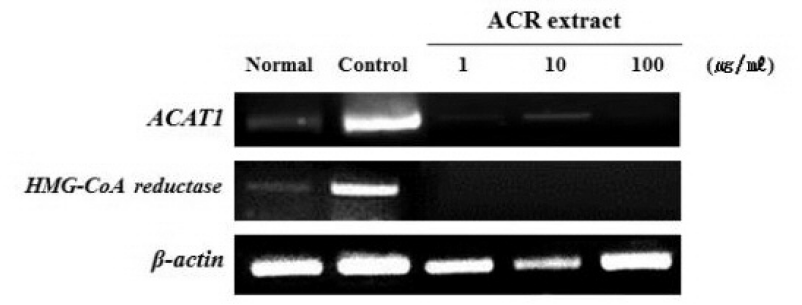
Effect of ACR extract on ACAT1 and HMG-CoA reductase mRNA expression in HepG2 cells.
ACAT1, HMG-CoA reductase and β-actin mRNA expression were determined using RT-PCR. Normal ; non-treated HepG2 cells, Control ;0.5 mM FAs (palmitate:oleic acid, 6:4)-treated HepG2 cells.