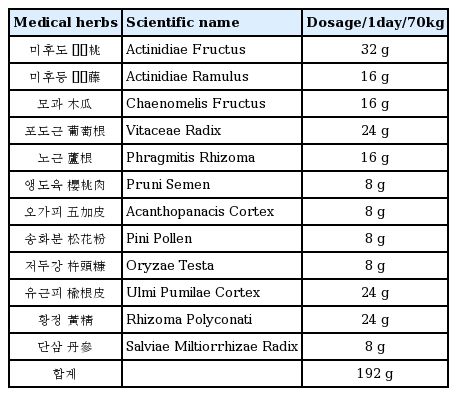
Effects of KMS on the DNCB induced animal Model of Atopic Dermartitis
Article information
Abstract
Objectives
The purpose of this study is to examine the effect of water and fermentation extracts of KMS (Kami-Mihudeongsikjang-tang) on AD (atopic dermatitis). Additionally, by applying the fermentation extracts of KMS at the first sensitization and latency period, I investgated whether it could prevent AD.
Methods
In this study, to test the effect and preventive efficacy of KMSs on AD. DNCB-induced BALB/c mice of AD model was used. Through histological observation, epidermis and dermis thickness, the infiltration of eoshiphils and mast cells in epidermis and dermis were examined. We measured the serum level of IgE and IL-6, TNF-alpha, and the expressions of NF-κB and MAPK protein. In order to examine the effect of KMSs on keratinocyte, HaCaT cells were treated TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma to induce an inflammatory response. The KMSs were applied at various concentration in the experimental group. We investigated TARC expression.
Results
The treatment groups were reduced epidermis and dermis thickness, inhibited the infiltration of eosinophils and mast cells, reduced the serum level of IL-6. Moreover, sfKMS group reduced serum level of TNF-alpha, inhibited the protein expressions of NF-κB and the phosphoryllation of ERK, JNK and p38. Especially sfKMS-pre group were reduced the serum level of IgE, show significant inhibition on the protein expression of NF-κB and the phosphoryllation of ERK, JNK and p38. In the experiment on HaCaT cells, sfKMS group were reduced expression of TARC.
Conclusions
These result suggest that wKMS and sfKMS was effective in the treament on AD, and sfKMS would prevent AD.
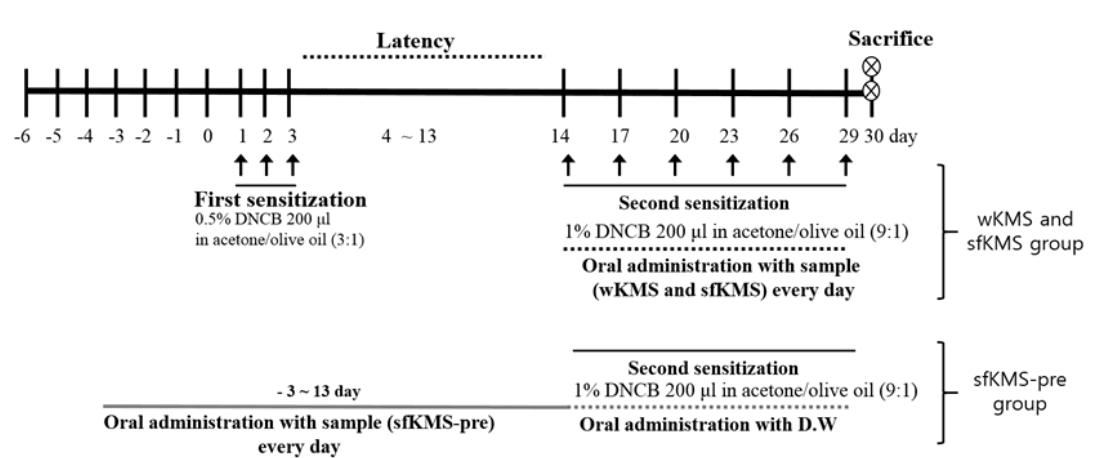
Experimental schedule for induction of atopic dermatitis. All topical applications were applied to the dorsal skin. The normal group was treated with a PBS.
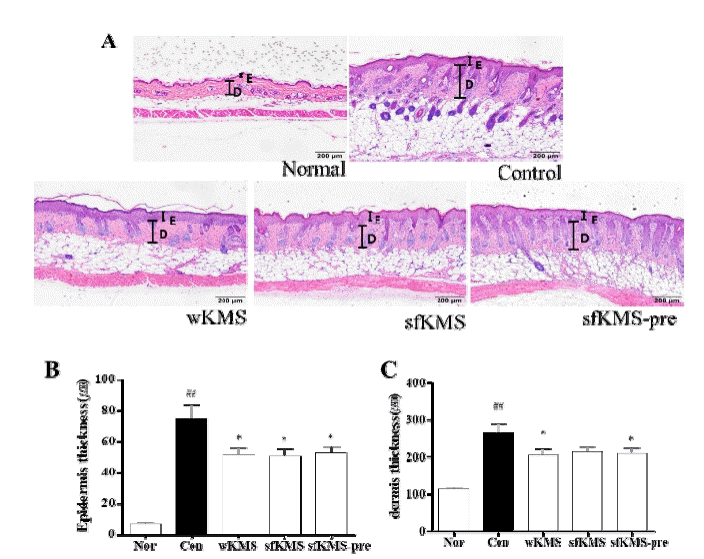
The effects of KMSs on epidermis and dermis thickness change in dorsal skin tissue of DNCB-induced BALB/c mice. (A) The thicknesses of epidermis and dermis were identified by H&E staining at magnification 100× (scale bar 200μm). (B) Measurement of epidermis thickness. (C) Data of dermis thickness. Each data represents the mean ± SEM. ##p < 0.01 compared with normal and *p < 0.05 compared with control. E: epidermis: D: dermis. KMS, kami-Mihudeongsikjang-tang. DNCB, 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene.
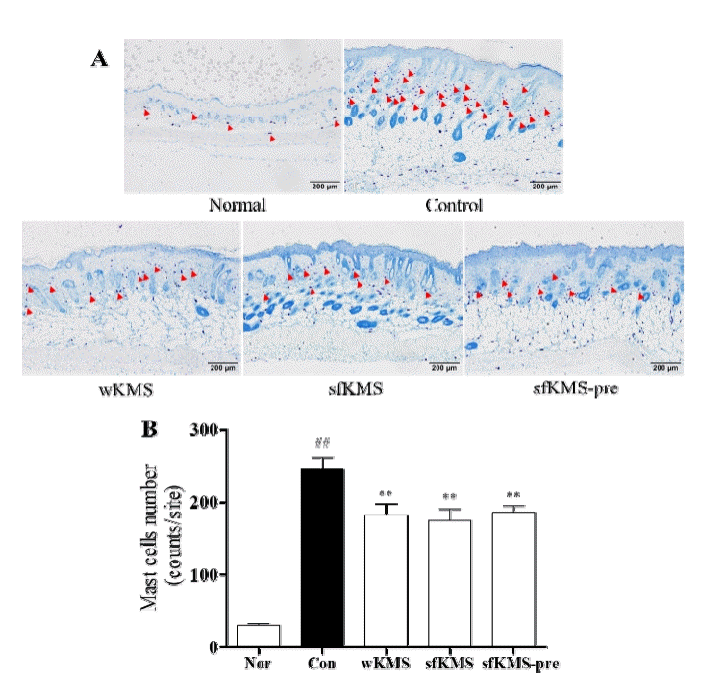
The effects of KMSs on mast cell infiltration in dorsal skin tissue of DNCB-induced BALB/c mice. (A) The infiltration of mast cell in epidermis and dermis lesions were examined by toluidine blue staining of skin section (magnification: 100′, scale bar: 200μm). (B) The number of mast cell. The infiltration of mast cell in three sites was counted. Each data represents the mean ± SEM. ##p < 0.01 compared with normal and **p<0.01 compared with control. KMS, kami-Mihudeong sikjang-tang. DNCB, 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene.
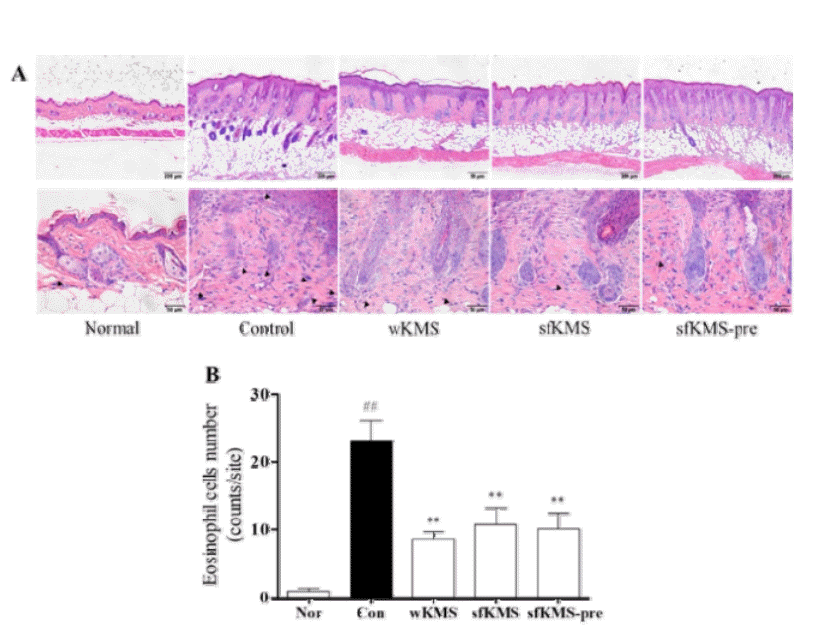
The effects of KMSs on eosinophil infiltration in dorsal skin tissue of DNCB-induced BALB/c mice. (A) The infiltration of eosinophil in epidermis and dermis lesions were examined by H&E staining of skin section (magnification: 100′ and 400′, scale bar: 200μm and 50μm). (B) The number of eosinophil. The infiltration of eosinophil in six sites was counted. Each data represents the mean ± SEM. ##p < 0.01 compared with normal and **p<0.01 compared with control. KMS, kami-Mihudeongsikjang-tang. DNCB, 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene.
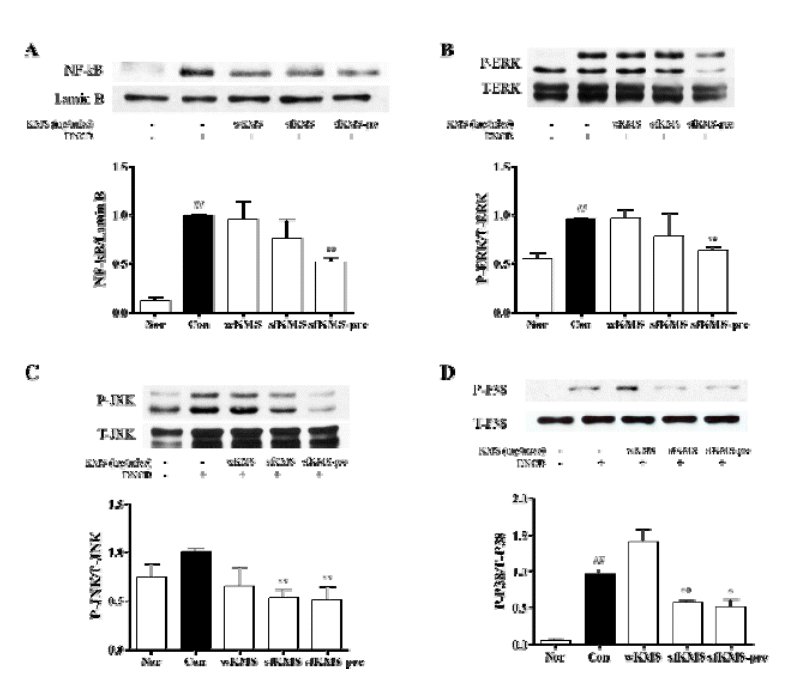
The effects of KMS on NF-kB and MAPKs expressions was investigated by western blot. (A) The level of NF-kB (B) P-ERK, (C) P-JNK, (D) P-P38 expressions were examined by western blot. The expression level were measured by image J. Each data represents the mean SEM. ##p < 0.01 compared with normal and **p < 0.01, *p<0.05 compared with control. KMS, kami-Mihudeongsikjang-tang. NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells.. MAPK, Mitogen-activated protein kinase. ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase. T-ERK, total-ERK. P-ERK, phospho-ERK. T-JNK, total-JNK. P-JNK, phospho-JNK. T-p38, total-p38. P-p38, phospho-p38.
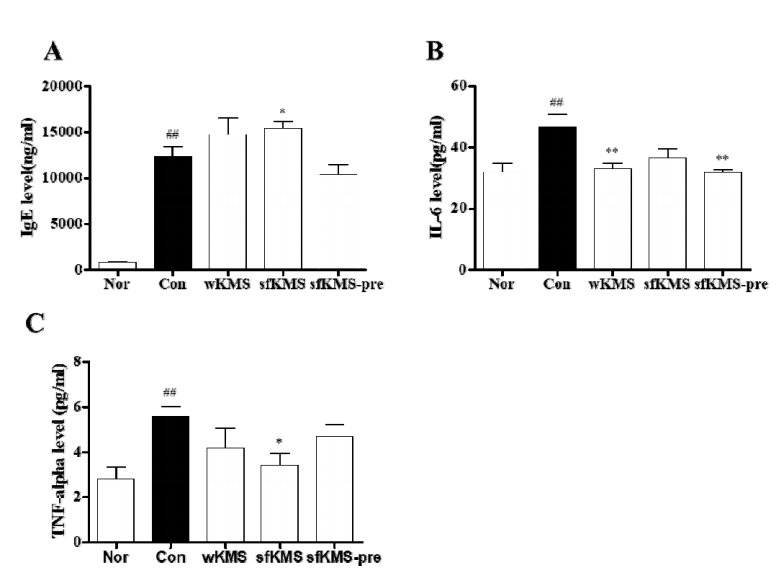
The effects of KMSs on IgE and cytokines level in serum of DNCB-induced BALB/c mice. (A) The data of serum IgE (B) IL-6 (C) TNF-alpha. Each data represents the mean ± SEM. ##p< 0.01 compared with normal and **p < 0.01, *p <0.05 compared with control. KMS, kami-Mihudeongsikjang-tang. IgE, immunoglobulin E. IL-6, interleukin 6, TNF-alpha, tumor necrosis factor-alpha.
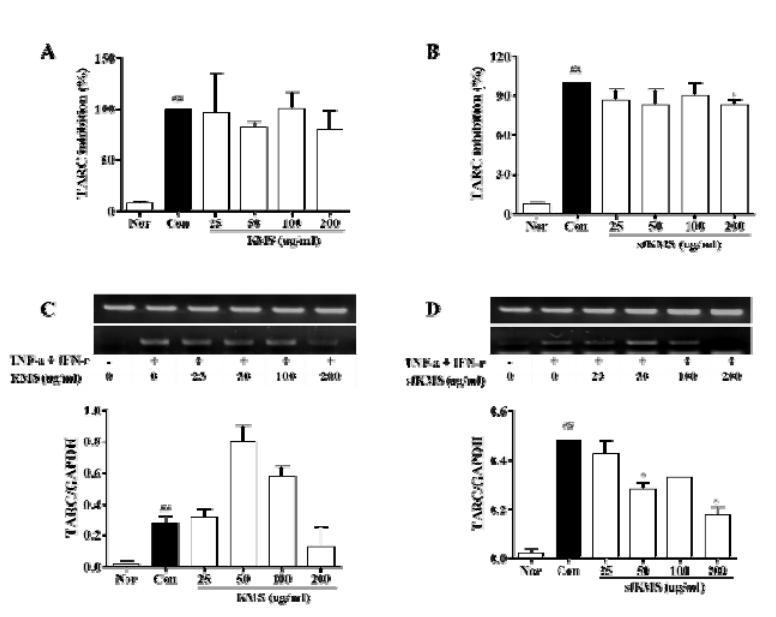
The effects of KMS and sfKMS on TARC expressions. (A-B) ELISA, (C, D) RT-PCR. Each data represents the mean SEM. ##p < 0.01 compared with normal and *p < 0.05 compared with control. KMS, kami-Mihudeongsikjang -tang. TARC, thymus and activation-regulated chemokine. RT-PCR, Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction.