Effects of 『Geum-Gwe-Yo-Ryak(金匱要略)』 Prescription for Chest Pain Including Kwaruhaebaekbanha-tang and Kwaruhaebaekpaekju-tang on Macrophage Polarization
Article information
Abstract
Objectives
This study was designed to evaluate the macrophages polarization of traditional Korean medicine on cardiac pain about Geum-Gwe-Yo-Ryak’s two prescriptions including Kwaruhaebaekbanha-tang (KHB) and Kwaruhaebaekpaekju-tang (KHP).
Materials and methods
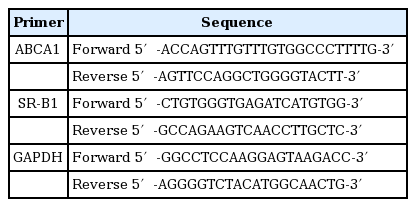
Flow cytometry analysis was used to measure the changes in the ratio of M1 type and M2 type macrophages. Protein expression of nuclear factor-like 2 (Nrf2), heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) were measured by Western Blot, and ABCA1 and SR-B1 were detected by real time PCR (RT-PCR). Intracellular lipid accumulation was measured by Oil Red O staining (ORO staining).
Results
KHB and KHP increase anti-oxidative activity related protein levels including Nrf2 and HO-1. Furthermore, KHB and KHP inhibit lipid accumulation on intracellular levels through induction of ATP binding receptor cassette subfamily A member 1 (ABCA1) and scavenging receptor class B member 1 (SR-B1), respectively. Finally, KHB and KHP also blocked pro-inflammatory mediators including tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFα) and interleukin-6 (IL-6), iNOS and COX-2 expression.
Conclusion
This study suggests that KHB and KHP potently regulate the M1/M2 macrophage polarization.
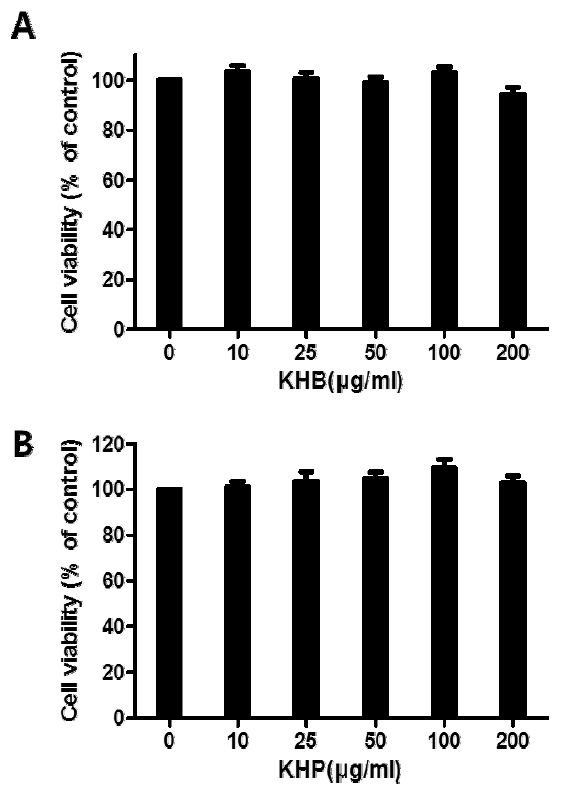
The effect of KHB (A) and KHP (B) on cell viability in human monocytic THP-1 cell line. Cell viability was determined using the cell viability assay kits (Ez-CyTox). All data represent the means±SD of three different experiments.
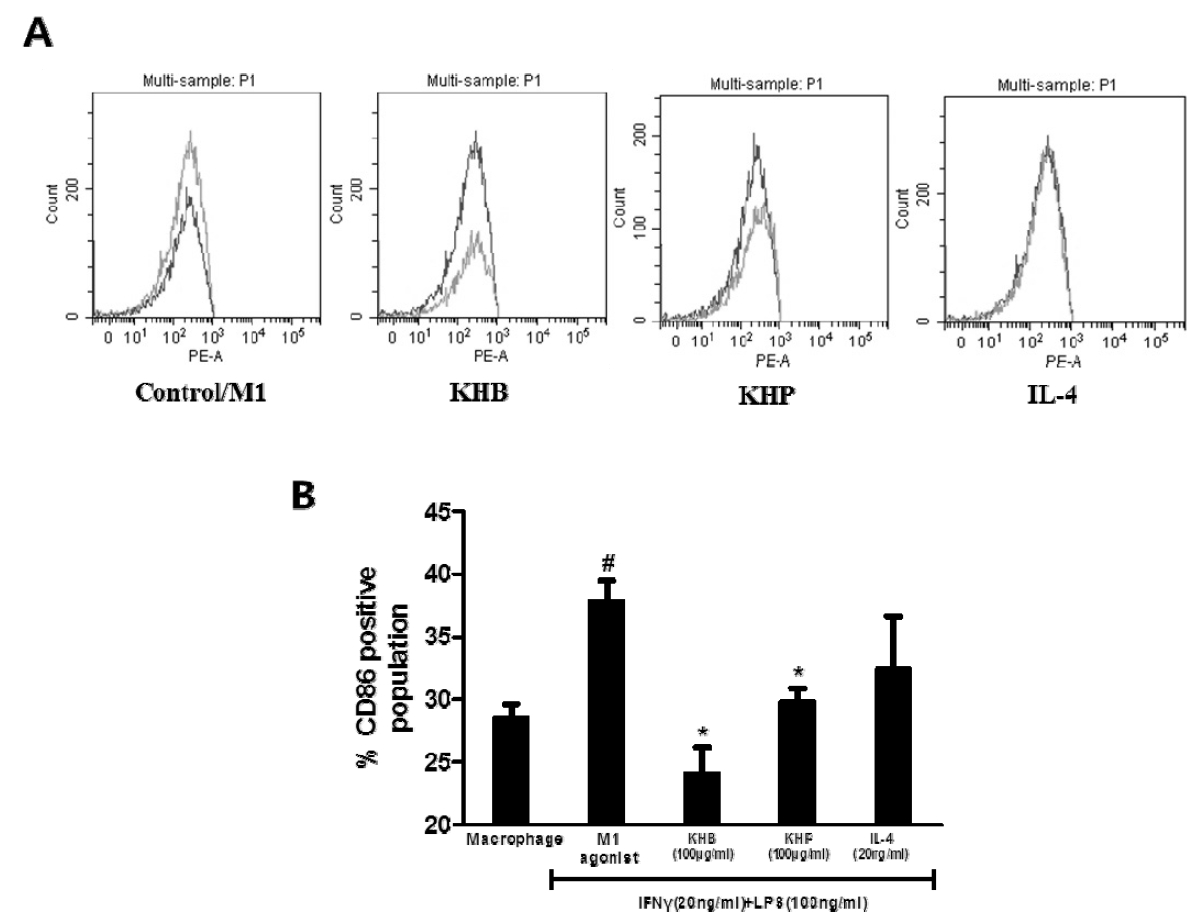
The effect of KHB and KHP on expression of CD86 levels in M1 polarized THP-1 cells. Flow cytometry analysis (A) and CD86 population levels (B) on IFNγ (20ng/ml) and LPS (100ng/ml)-stimulated THP-1 cells. All data represent the means±SD of three different experiments. #P < 0.05 compared to untreated cells, and asterisk indicates statistically significant difference between polarized group (*< 0.05).
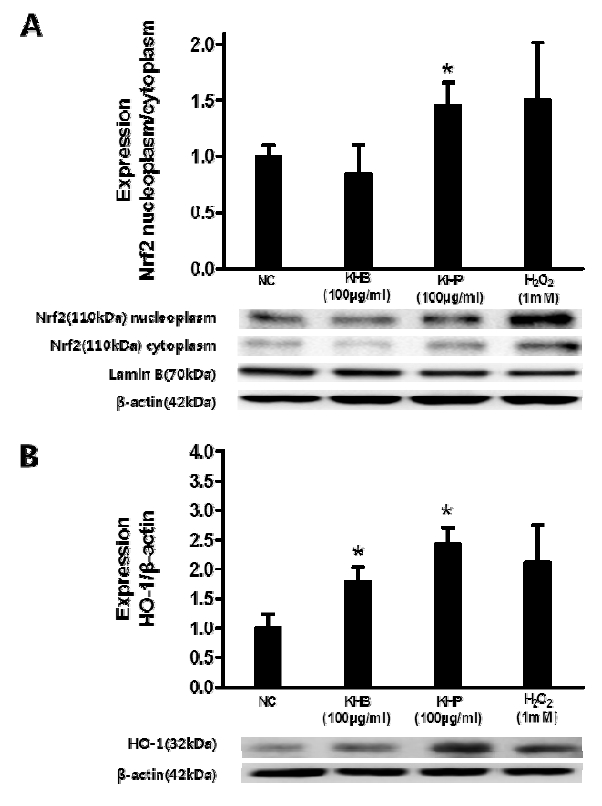
The effect of KHB and KHP on antioxidant-related protein expressions including Nrf2 (A) and HO-1 (B). All data represent the means±SD of three different experiments. Asterisk indicates statistically significant difference between untreated group (* < 0.05).
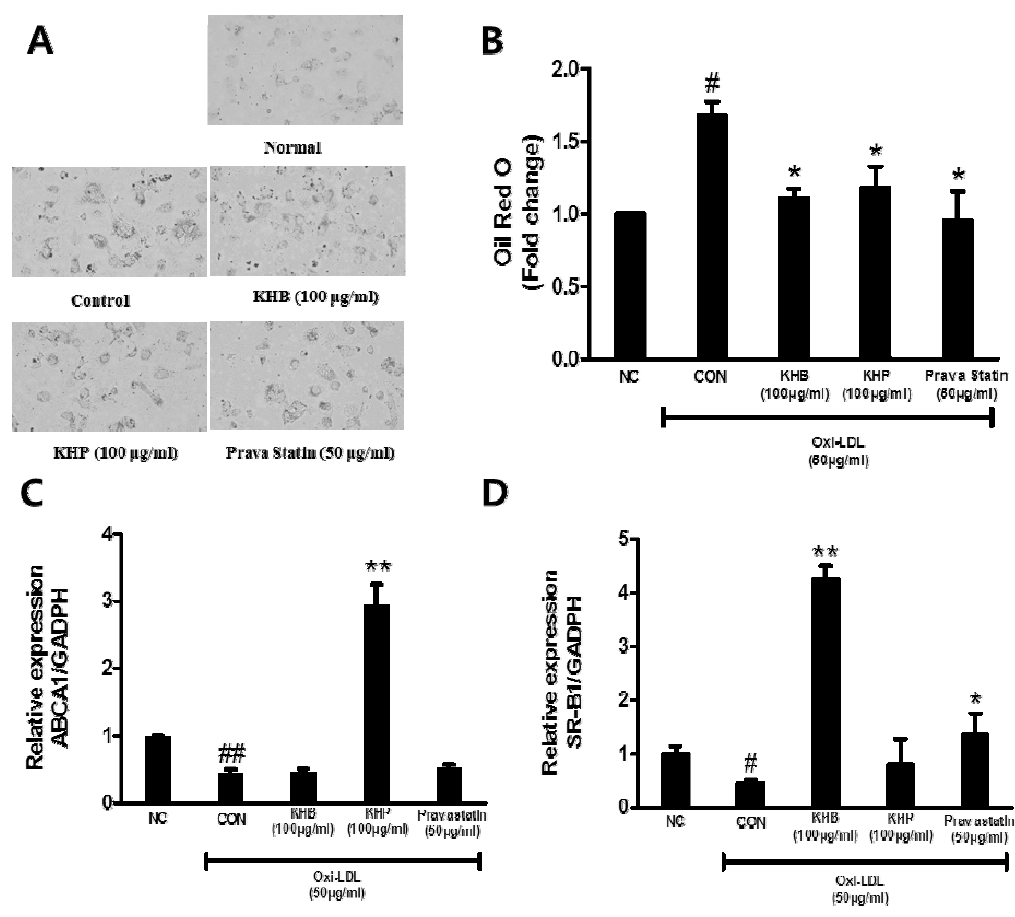
The effect of KHB and KHP on oxi-LDL-stimulated lipid accumulation. Microscopic images (A) and resultant solution were measured at 520 nm under microplate reader (B). Rever cholesterol-related genes expression were detected by quantitative real-time PCR including ABCA (C) and SR-B1 (D). All data represent the means ±SD of three different experiments. #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 compared to oxi-LDL untreated cells. Asterisk indicates statistically significant difference between ox-LDL-stimulated group (* < 0.05, ** < 0.01).
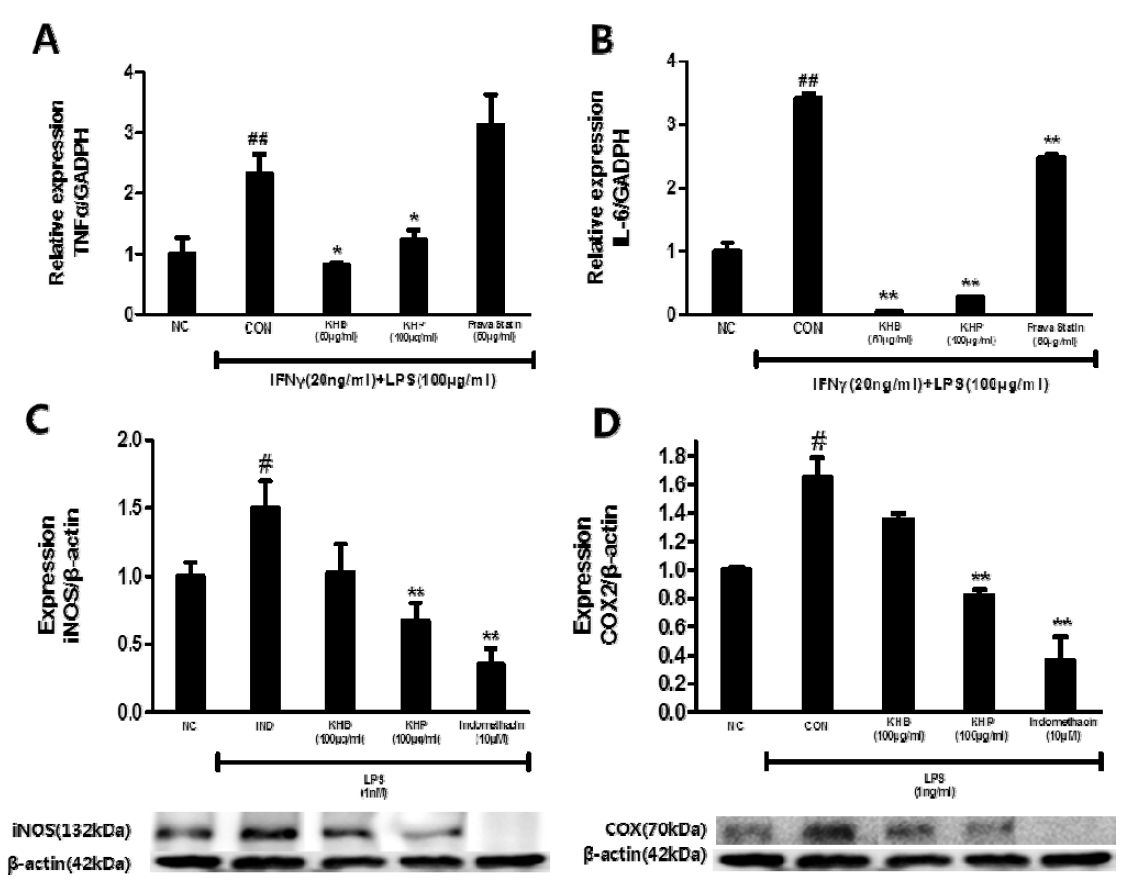
The effect of KHB and KHP on anti-inflammation-related mediator expressions including TNF-α (A), IL-6 (B), iNOS (C) and COX-2 (D). #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 compared to oxi-LDL untreated cells. Asterisk indicates statistically significant difference between ox-LDL-stimulated group (* < 0.05, ** < 0.01).