Effects of Jeungmiobi-tang on the Articular Cartilage Injuries Induced by Monosodium Iodoacetate in Rats
Article information
Abstract
Objectives
This study was carried out to investigate the protective effects of Jeungmiobi-tang on the articular cartilage injuries induced by monosodium iodoacetate in rats.
Methods
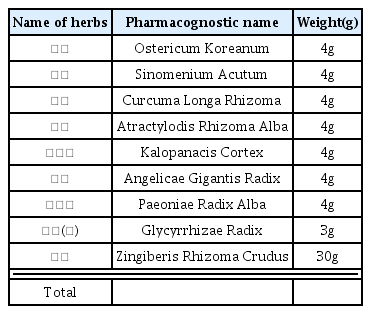
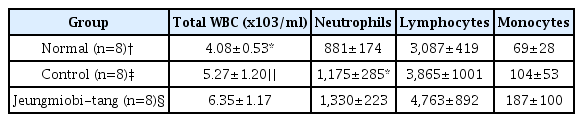
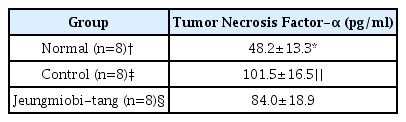
Twenty four rats were divided into three groups. Rats of normal group (n=8) were injected with 0.1 ml physiological saline into both knee joint cavities. In the rats of control group (n=8) and Jeungmiobi-tang group (n=8), Arthritis was induced by injecting with 0.1 ml monosodium iodoacetate (5 mg/ml) into both knee joint cavities. After the experiment, Gross and histopathological examinations on the knee joint were performed. The content of proteoglycan in articular cartilage and TNF-α and IL-1β in synovial fluid were also analyzed.
Results
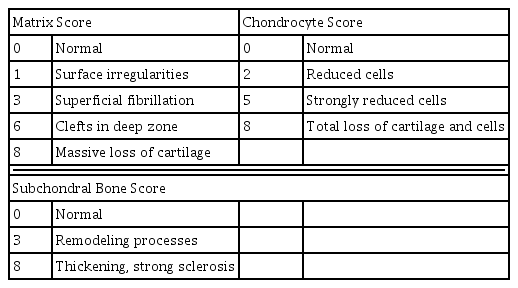
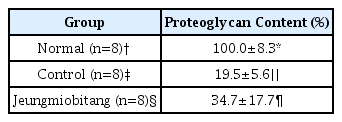
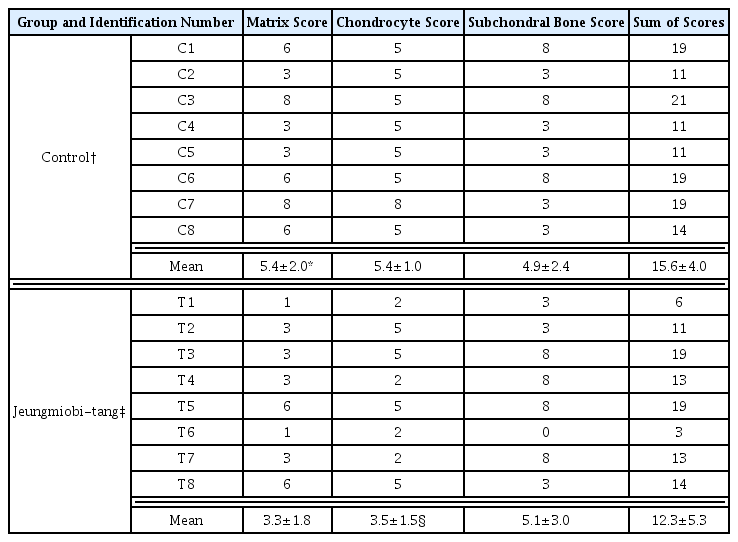
Grossly, Injuries to the articular cartilage surface was observed weak in the Jeungmiobi-tang group compared to the control group. Proteoglycan content in the articular cartilage was significantly higher in the Jeungmiobi-tang group than in the control group. The chondrocyte score was significantly lower in the Jeungmiobi-tang group than in the control group.
Conclusion
According to these results, that Jeungmiobi-tang has protective effects on the articular cartilage injuries induced by monosodium iodoacetate in rats.
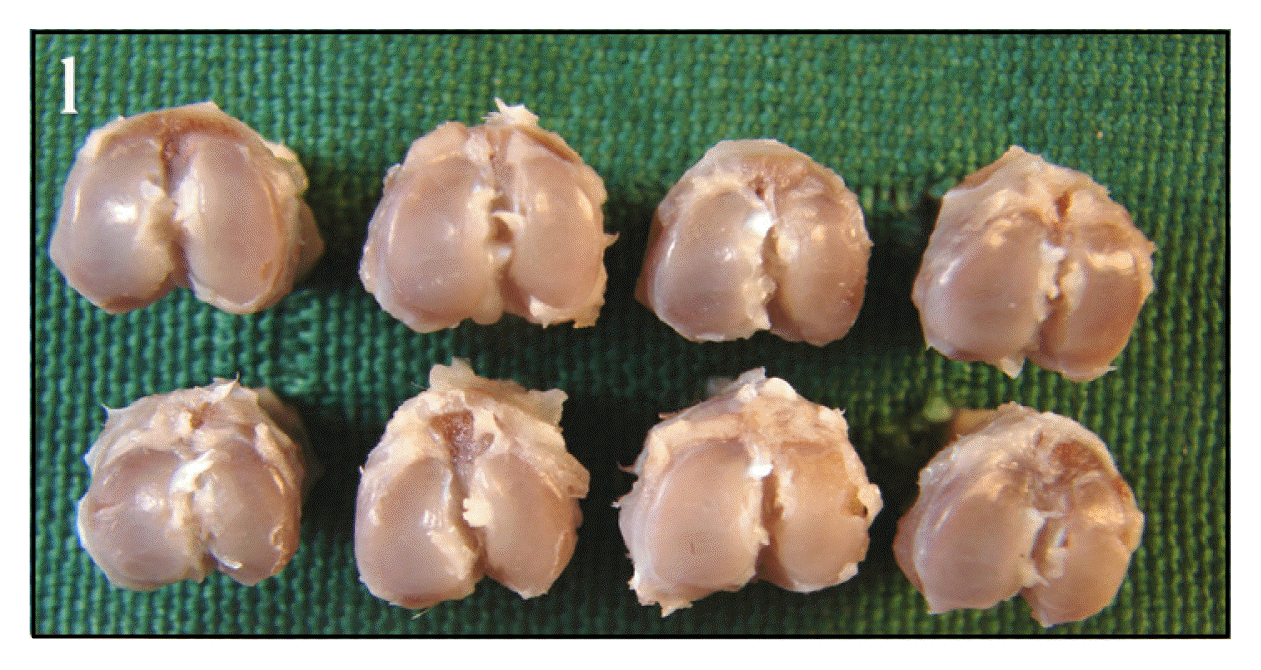
Picture of proximal tibia of normal group. The articular cartilage surfaces of tibia are glossy and smooth.
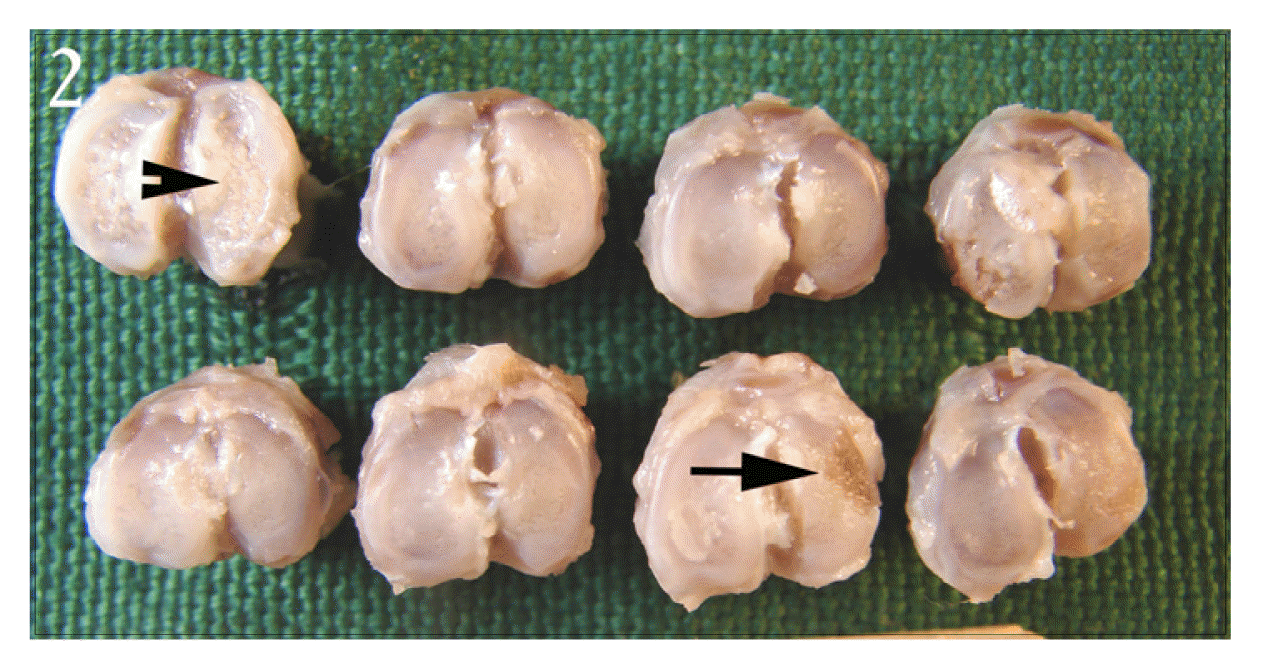
Picture of proximal tibia of control group. The articular cartilage surfaces of tibia are discolored and rough(arrow head), and some areas are deeply ulcerated(arrow).
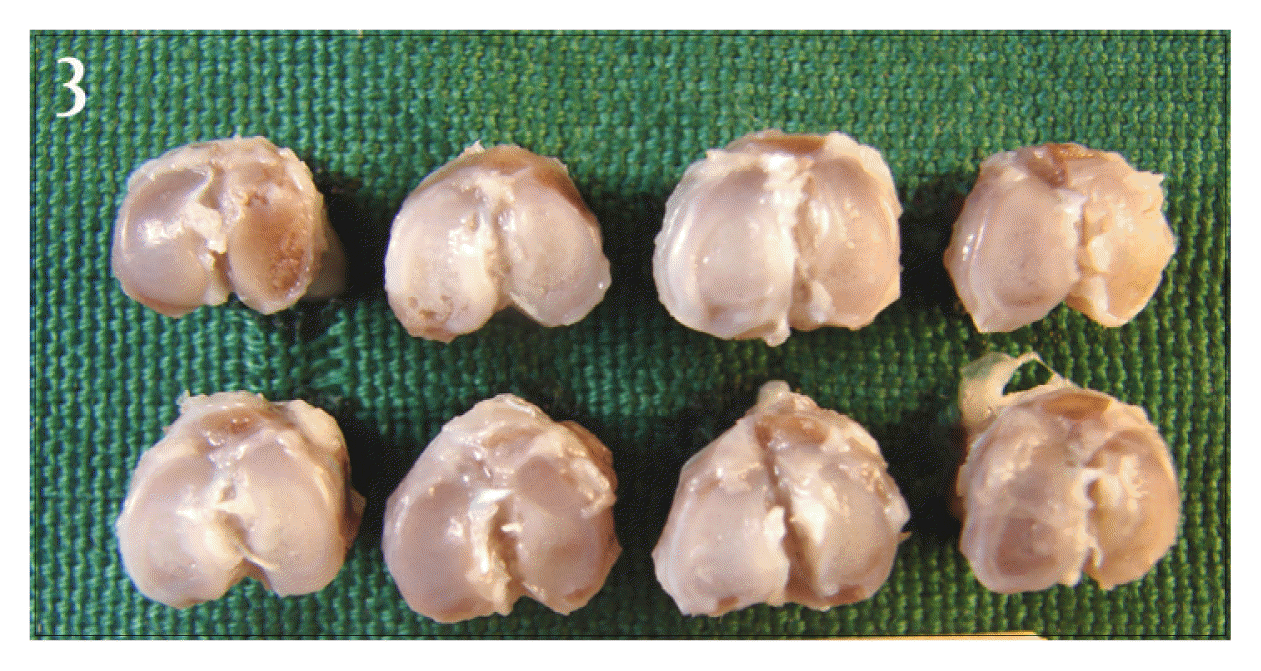
Picture of proximal tibia of Jeungmiobi-tang treated group. The articular cartilage surfaces of tibias are less discolored and less rough than control group.
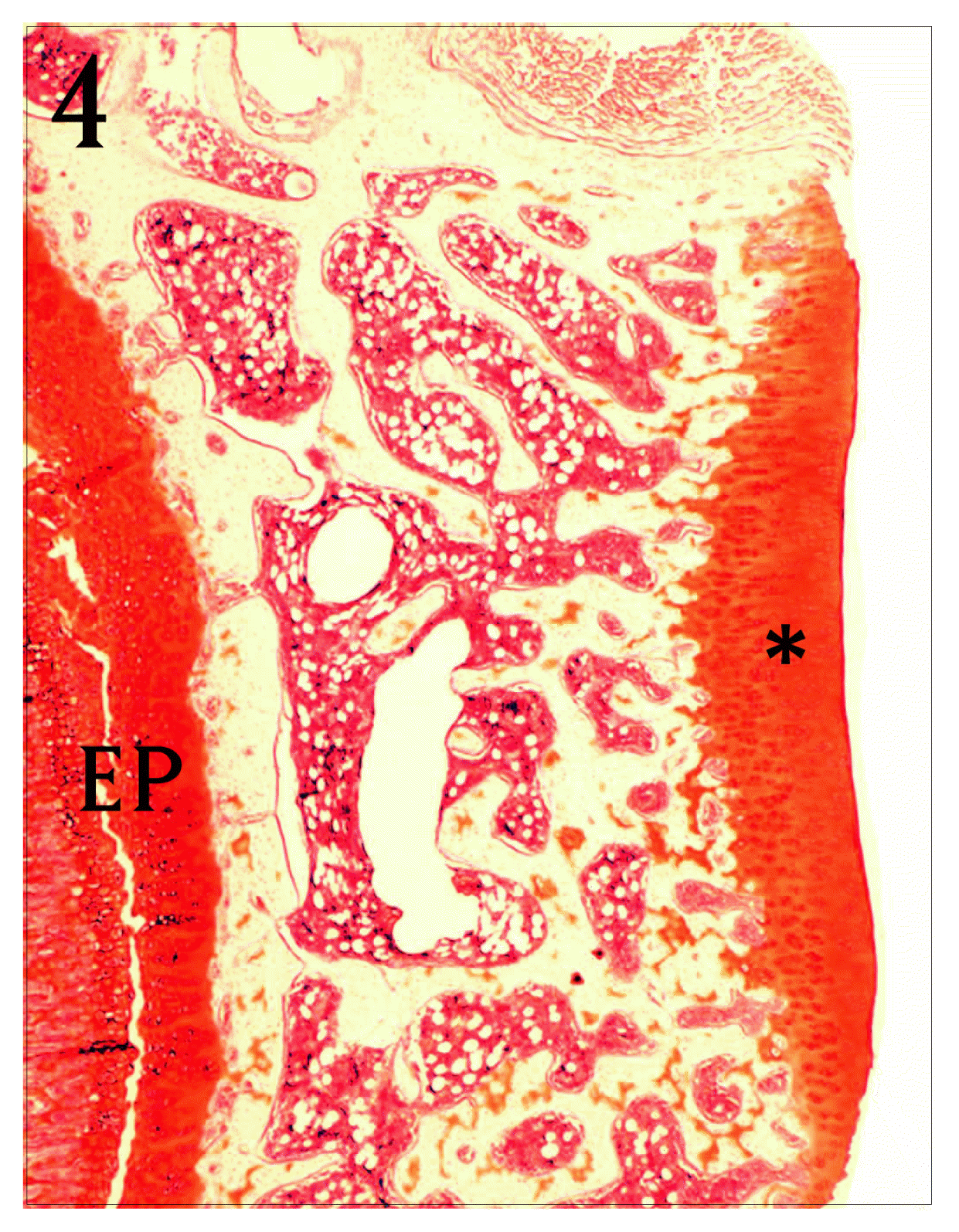
Coronal section of proximal tibia of normal group. The articular cartilage(*) is thickly stained with Safranine O. EP : epiphyseal plate, Safranine O stain, bar = 300 μm.
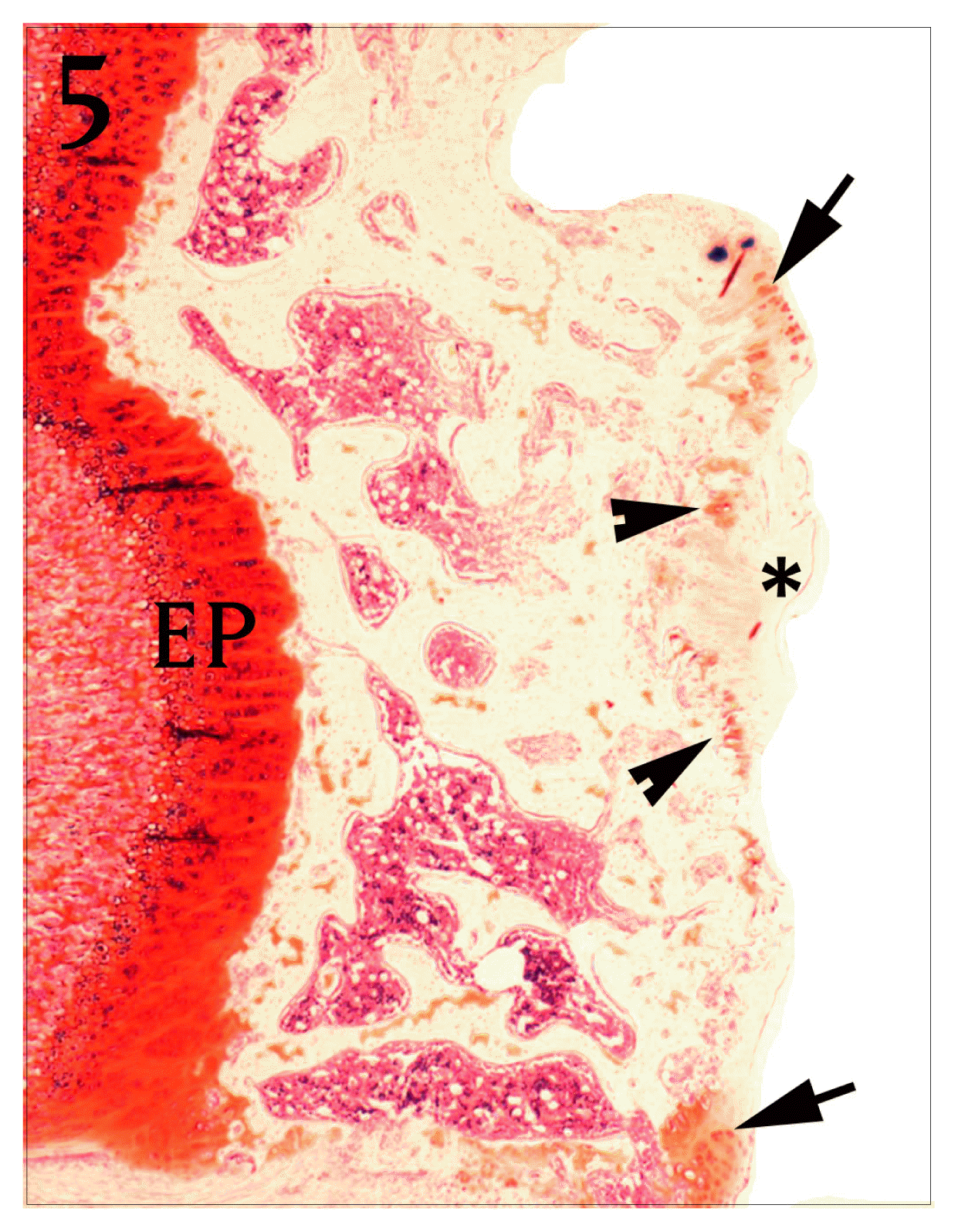
Coronal section of proximal tibia of control group. The red color disappeared in a great part of articular cartilage(*). Only a portion of the periphery of cartilage and subchondral part was stained red color(arrow and arrow heads). EP : epiphyseal plate. Safranine O stain, bar = 300 μm.
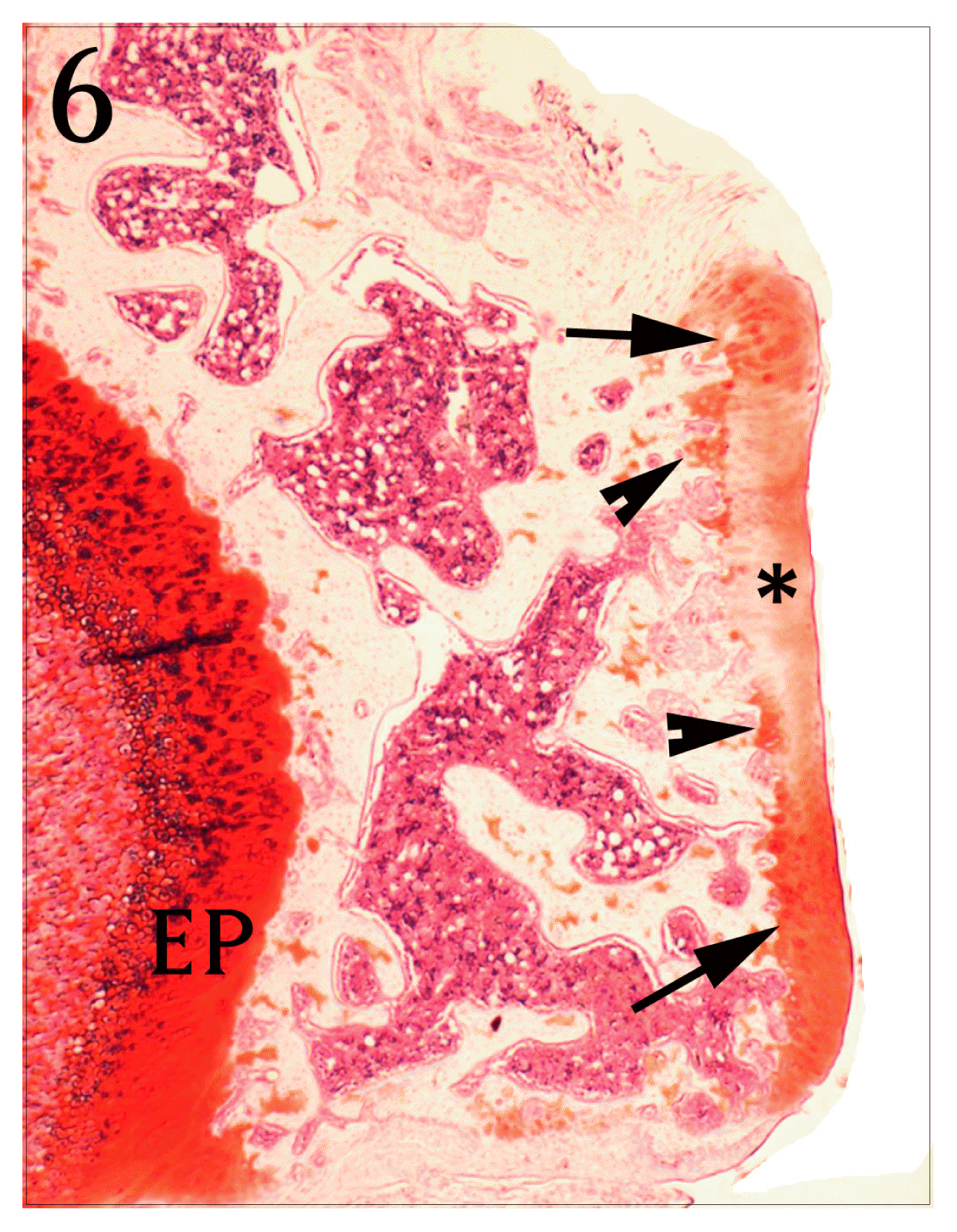
Coronal section of proximal tibia of Jeungmiobi-tang treated group. The articular cartilage(*) is more stained with Safranine O than control group(arrow and arrow heads). EP : epiphyseal plate. Safranine O stain, bar = 300 μm.

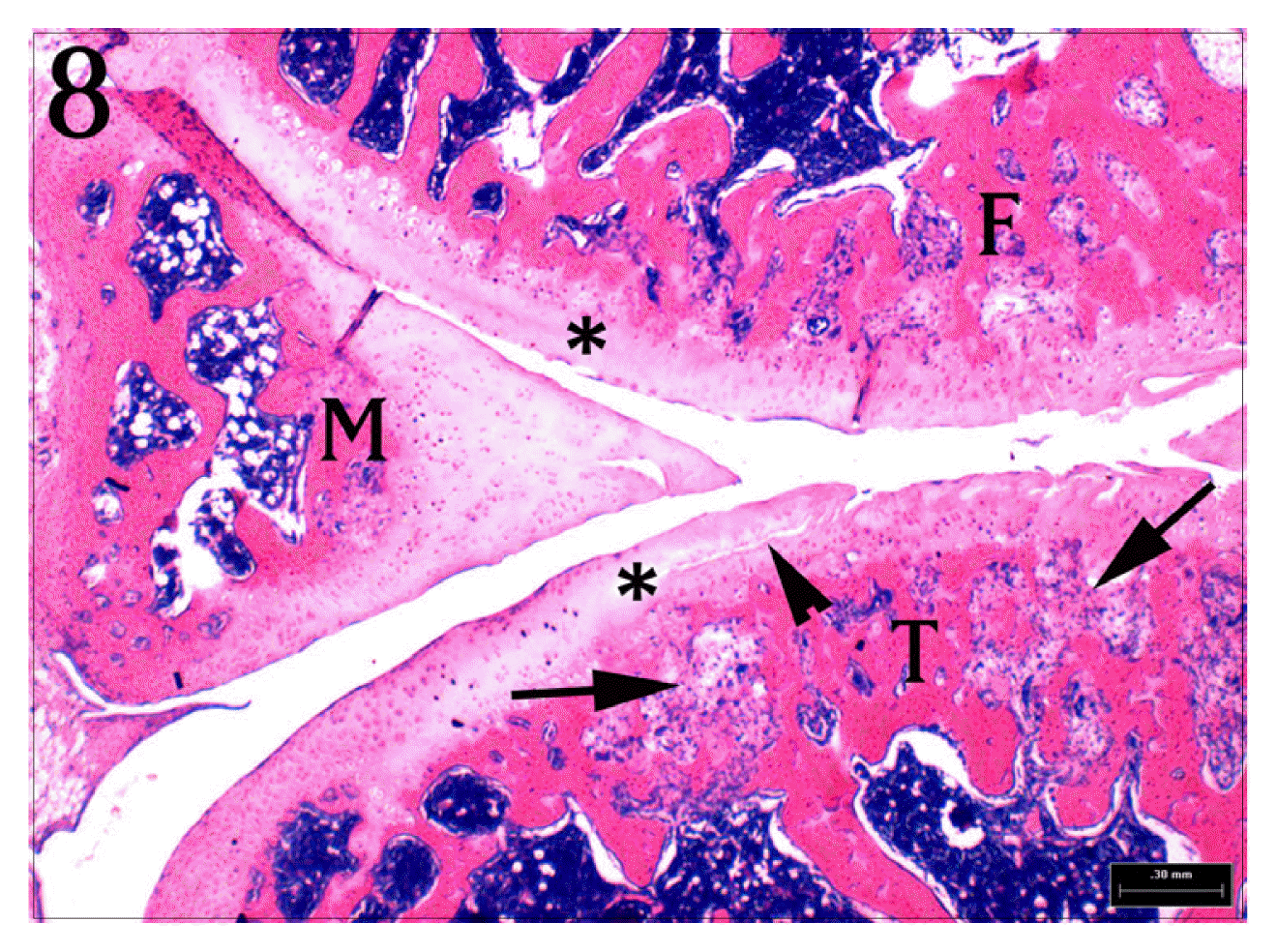
Sagittal section of normal group’s knee joint. The articular cartilages(*) of synovial membrane(arrows), meniscus(M), femur(F), tibia(T), and are normal. H&E stain, bar = 300 μm.
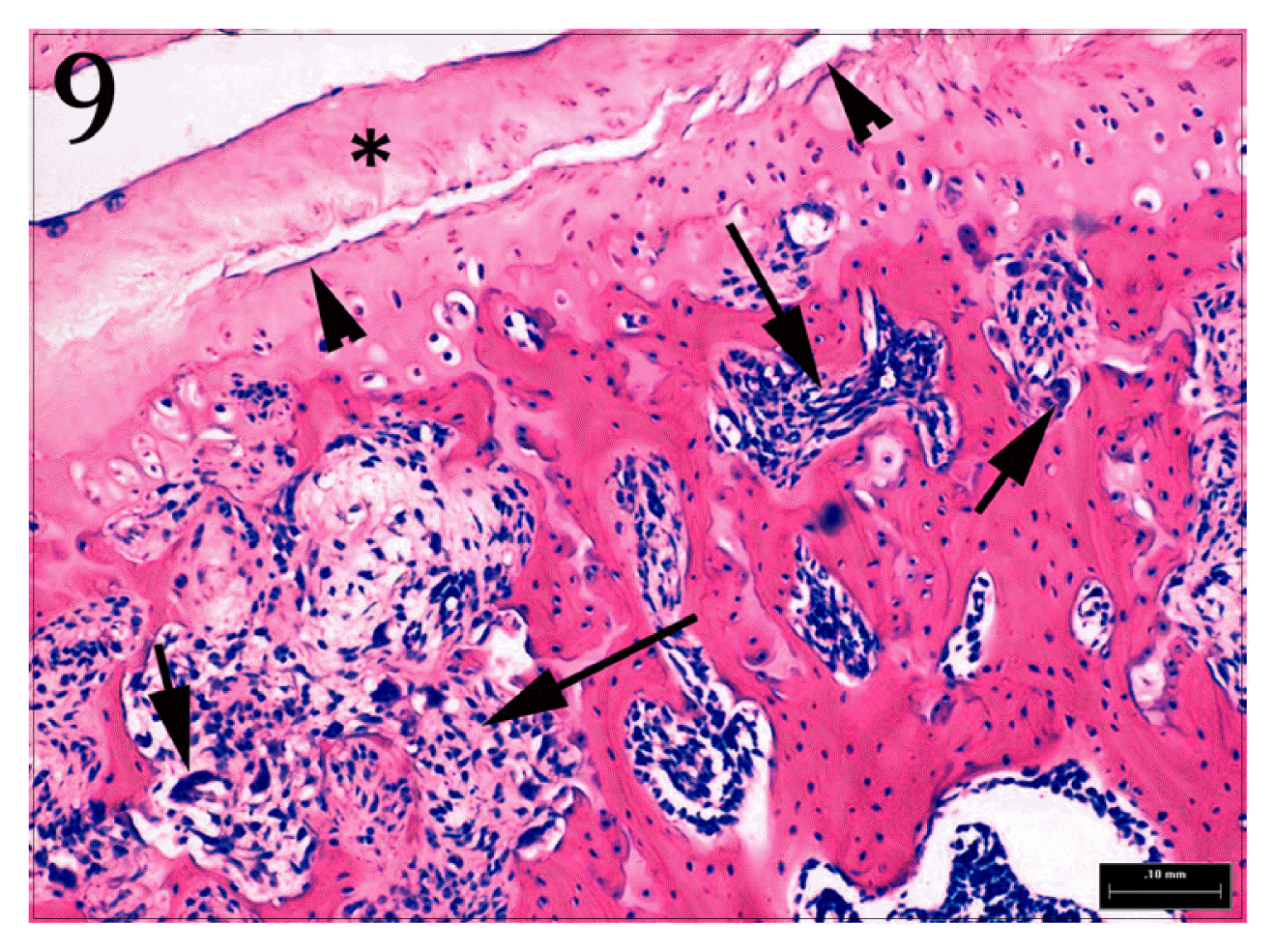
Higher magnification of Fig. 8. Clefts(arrow heads) and Homogenous degeneration(*) of articular cartilage are shown. Also, There are reactive fibrosis(long arrows) and activation of osteoclasts(small arrows). H&E stain, bar = 100 μm.
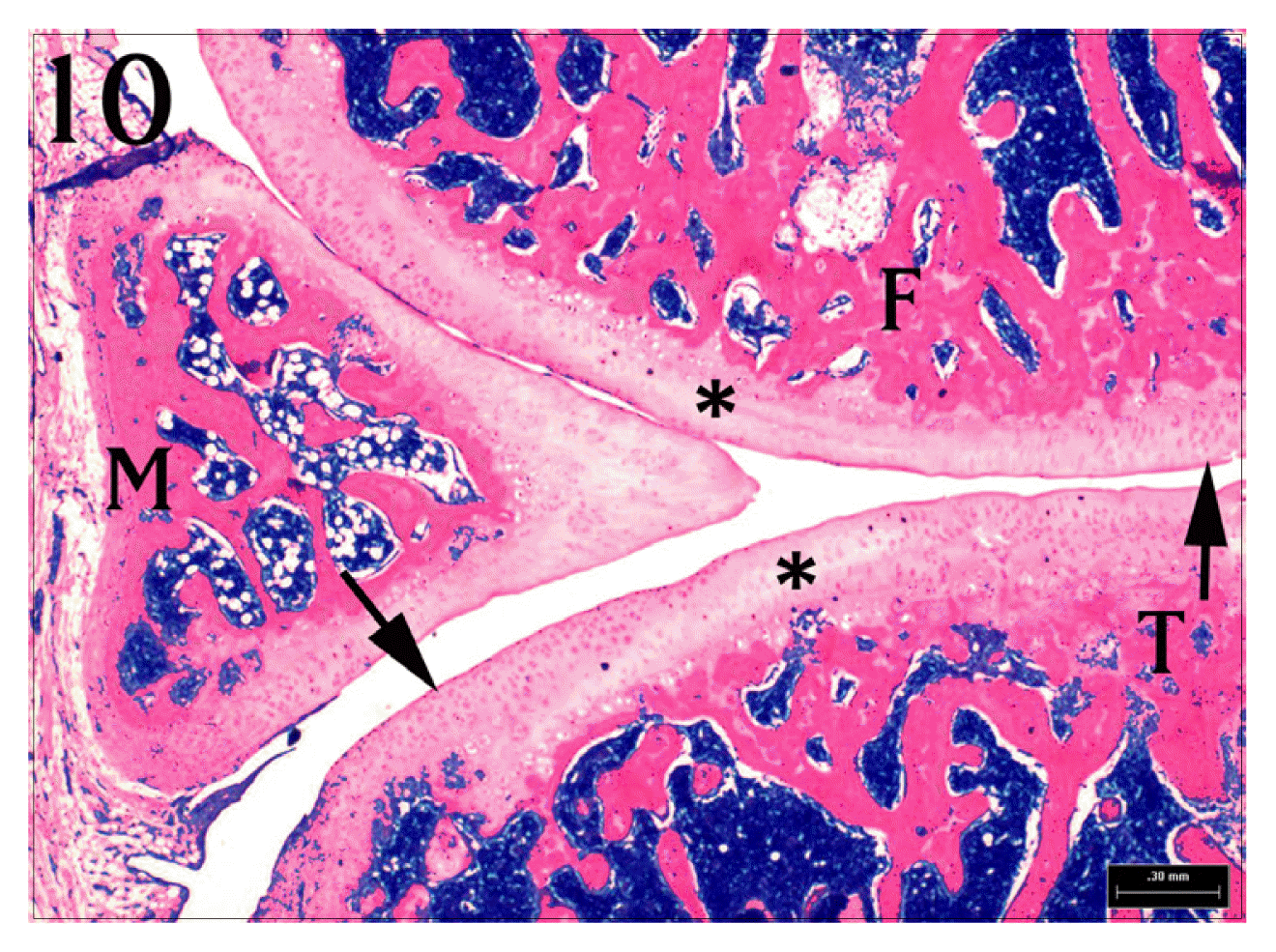
Sagittal section of Jeungmiobi-tang treated group’s knee joint. A great part of articular cartilages(*) of tibia(T) and femur(F) are degenerated. But chondrocytes (arrows) around the degenerative area are intact. Clefts in deep part of articular cartilage are not shown. H&E stain, bar = 300 μm.