The Anti-depressive Effect of Rehmanniae Radix Preparata via Anti-inflammatory Activity
Article information
Abstract
Objectives
Rehmanniae Radix Preparata (RRP) has been used as a traditional remedy to treat gynecology and endocrine diseases. Recently, studies on antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of RRP have been reported, so it was judged that RRP extracts would have an anti-depressive effect.
Methods
We investigated the anti-neuroinflammatory and anti-depressive effect of RRP on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced depression and LPS-stimulated BV2 microglia. RRP inhibited the LPS-stimulated excessive release of nitrite in the BV2 cells. RRP also significantly inhibited the inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, interleukin (IL)-1beta and IL-6 in LPS-stimulated BV2 microglial cells.
Results
RRP significantly suppressed the LPS-induced mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPKs) and nuclear factor (NF)-κB activation. In addition, administration of RRP not only inhibited the immobility time in the forced swimming test (FST) but also increased the total travel distance in the open field test (OFT). Also, RRP inhibited the elevation of TNF-alpha, IL-1beta, and IL-6 in brain of LPS-injected mice.
Conclusions
Considering the overall results, our study showed that RRP exhibited the anti-neuroinflammatory and anti-depressive activities via deactivation of MAPKs and NF-κB.
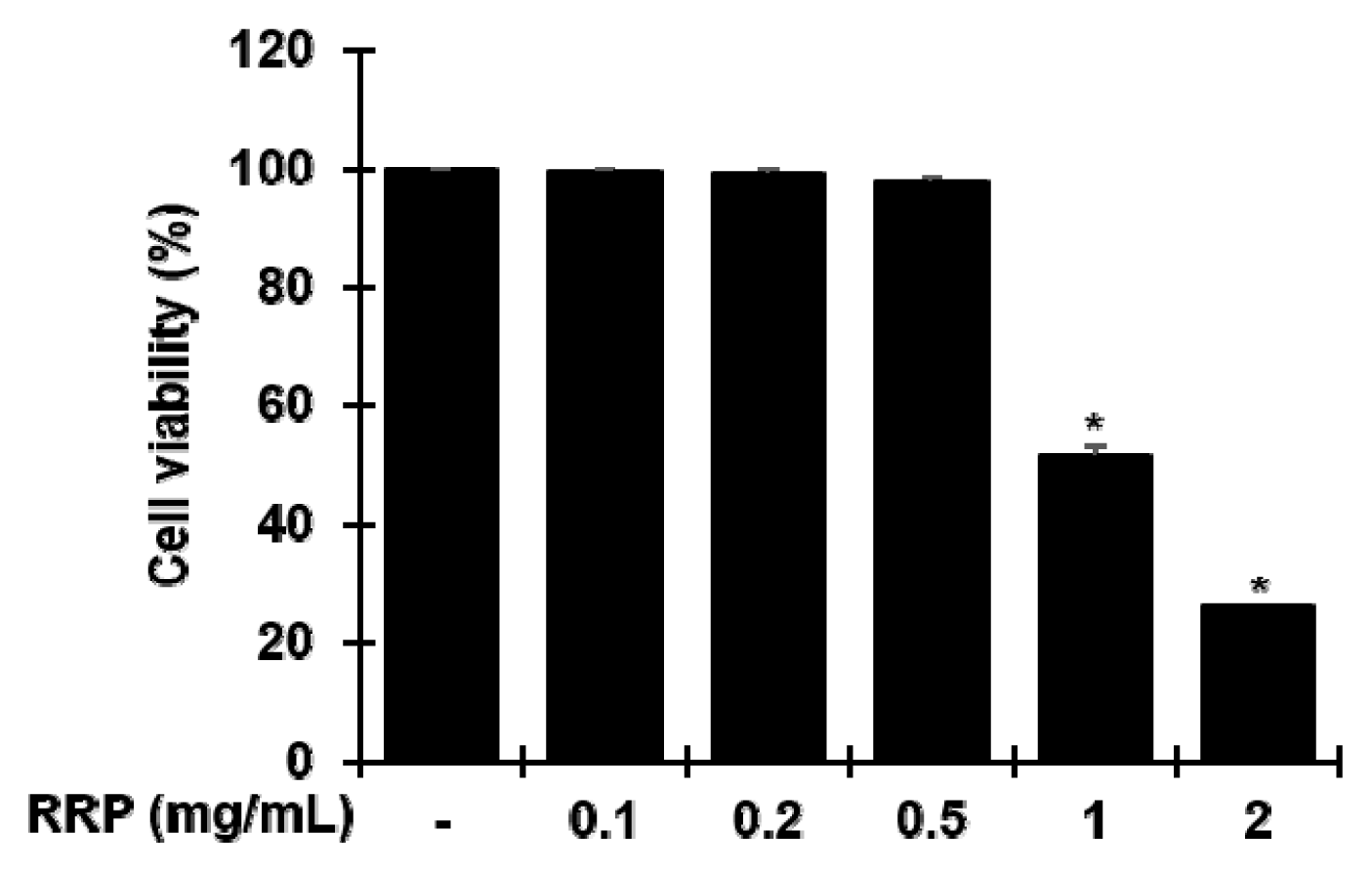
Effect of RRP on cell viability in BV2 cells.
Cells were treated with saline or the RRP (0.1, 0.2, 0.5, 1, and 2 mg/mL) for 24 h. Cell viability was determined by MTT assay, as described in Methods. Data are the mean ± S.D.(n = 3). *p < 0.05 versus the saline. RRP: Rehmanniae Radix Preparata.
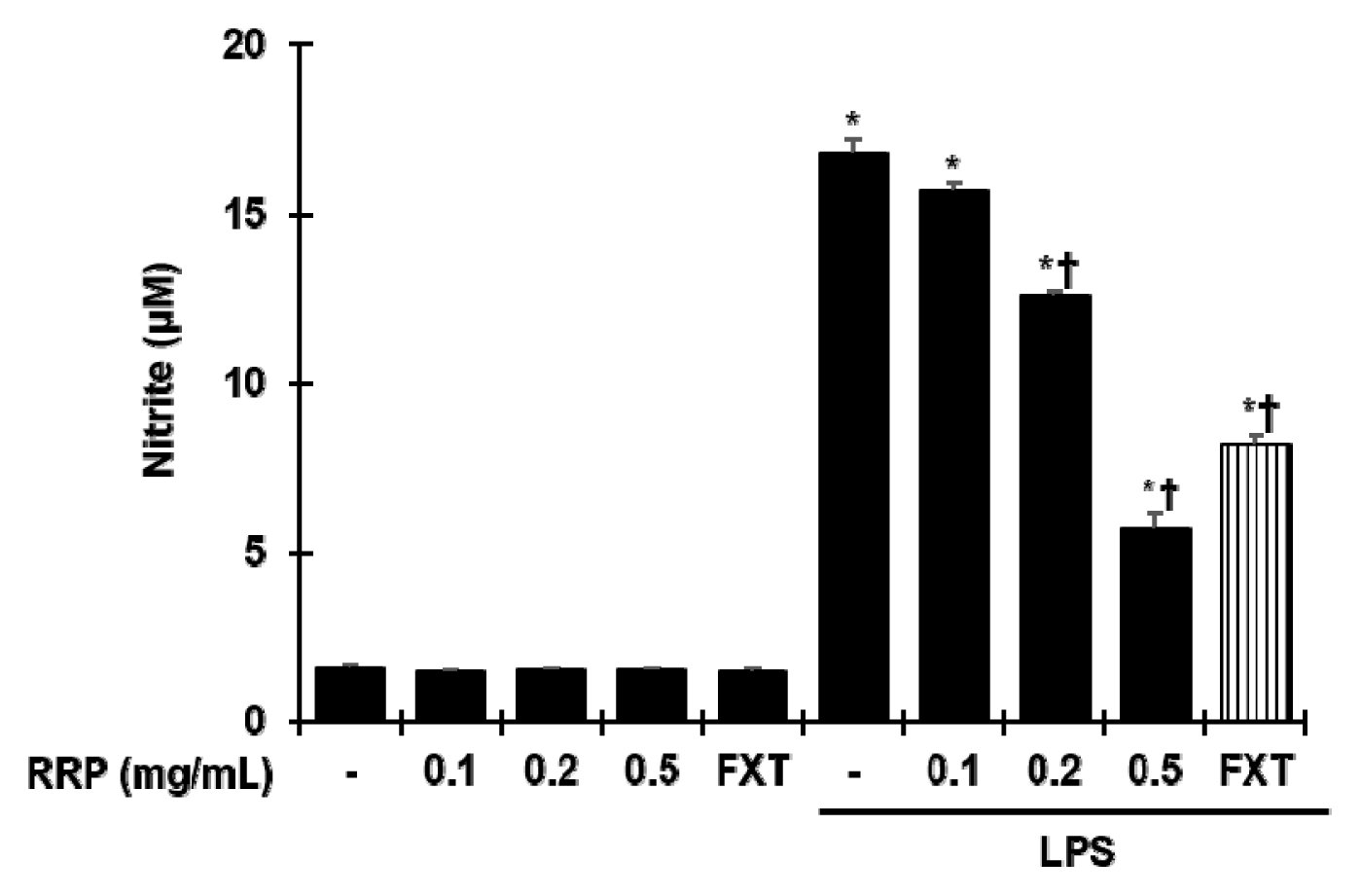
Effect of RRP on LPS-induced nitrite production in BV2 cells.
BV2 cells were incubated with saline, RRP(0.1, 0.2, and 0.5 mg/mL) or FXT(Fluoxetine 10 μM), and then stimulated with 1 μg/mL of LPS for 24 h. The concentrations of nitrite were determined by Griess reagent, as described in methods. Data are the mean ± S.D.(n = 3). *p < 0.05 versus the saline, †p < 0.05 versus LPS. RRP: Rehmanniae Radix Preparata, FXT: Fluoxetine.
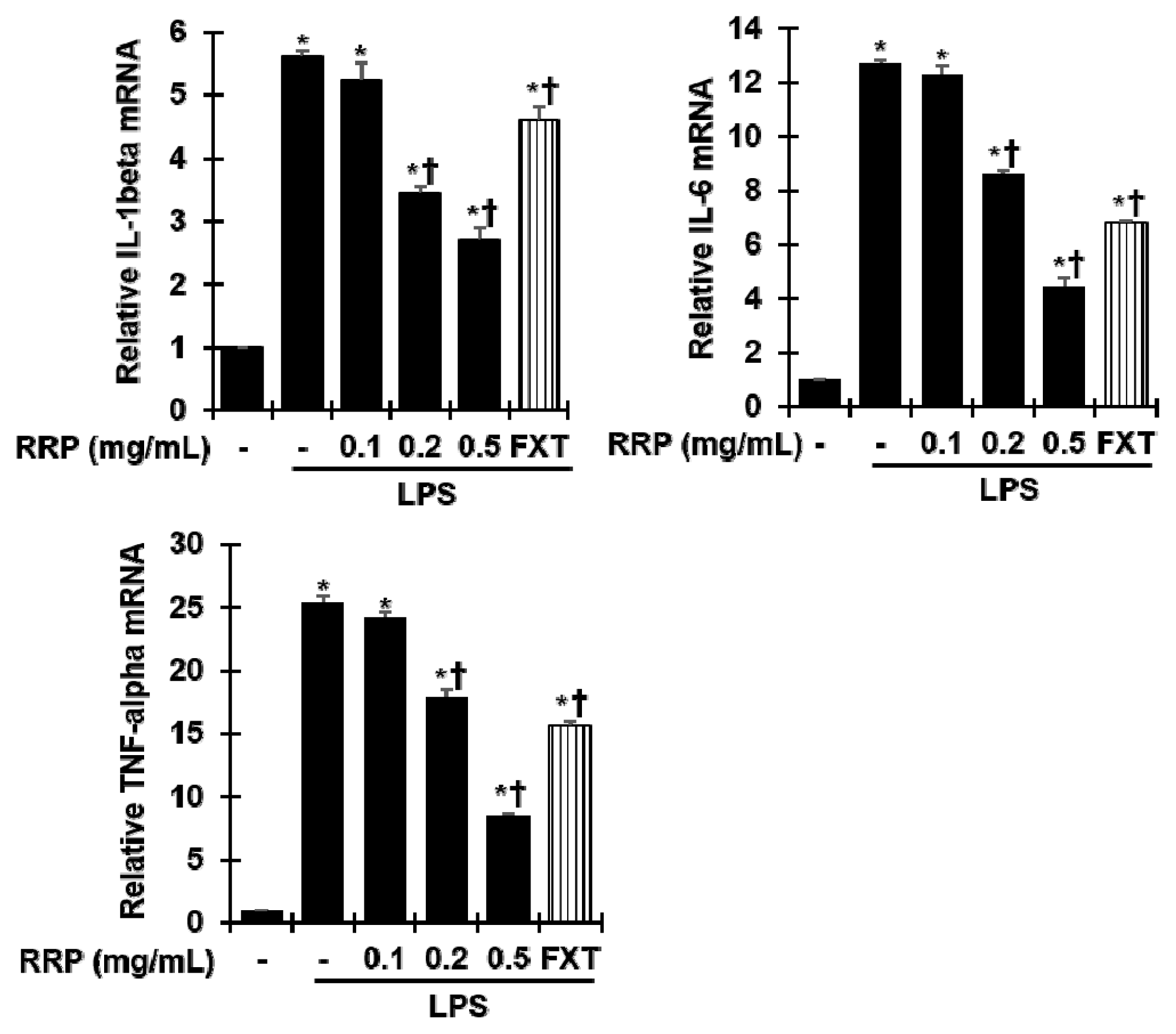
Effect of RRP on inflammatory cytokine expression in LPS-stimulated BV2 cells.
Cells were pre-treated with saline or RRP(0.1, 0.2, and 0.5 mg/mL) or FXT(Fluoxetine 10 μM) for 1 h and then stimulated with 1 μg/mL of LPS for 24 h. The mRNA expression level of IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α were measured by qPCR. Data are the mean ± S.D.(n = 3). *p < 0.05 versus saline, †p < 0.05 versus LPS. RRP: Rehmanniae Radix Preparata, FXT: Fluoxetine.
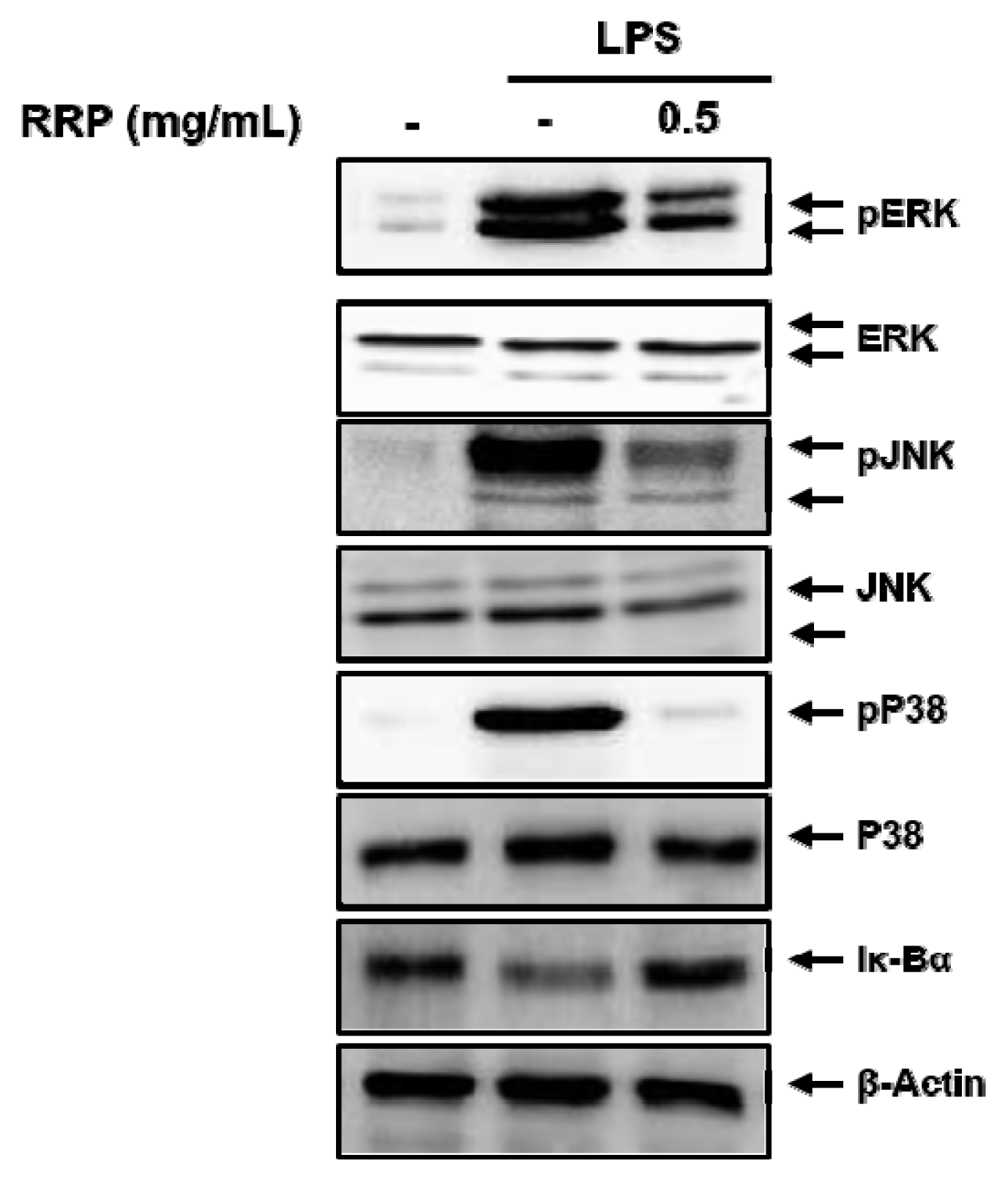
Effect of RRP on the activation of MAPKs and the degradation of Iκ-Bα in LPS-stimulated BV2 cells.
Cells were treated with the saline or RRP(0.5 mg/mL) for 1 h, and then stimulated with 1 μg/mL of LPS for 30 min. The protein expressions were measured by western blot. The experiment was repeated three times, and similar results were obtained. RRP: Rehmanniae Radix Preparata, FXT: Fluoxetine.
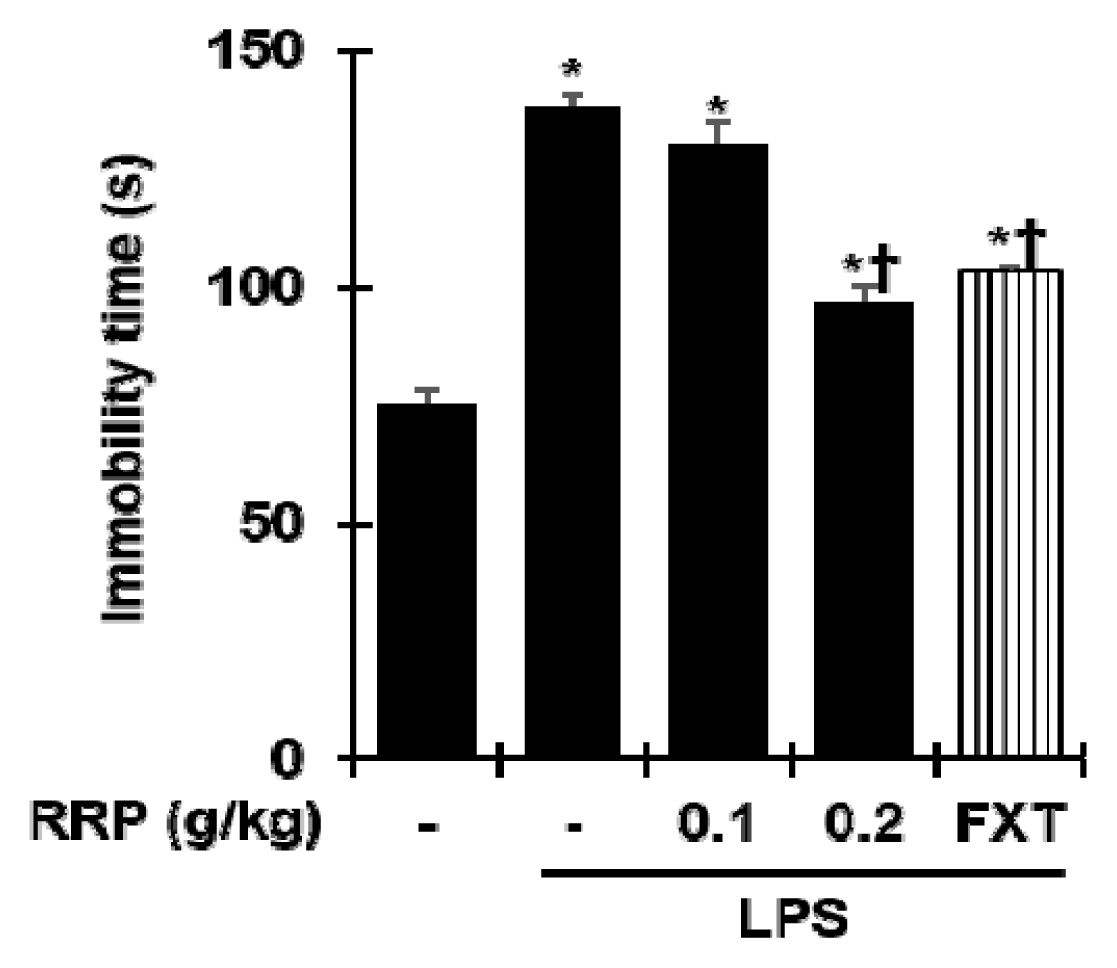
Effect of RRP on Force swimming test (FST) in the LPS-induced depressive-like behavior.
Data are the mean ± S.D.(n = 3). *p < 0.05 versus saline, †p < 0.05 versus LPS. RRP: Rehmanniae Radix Preparata, FXT: Fluoxetine.
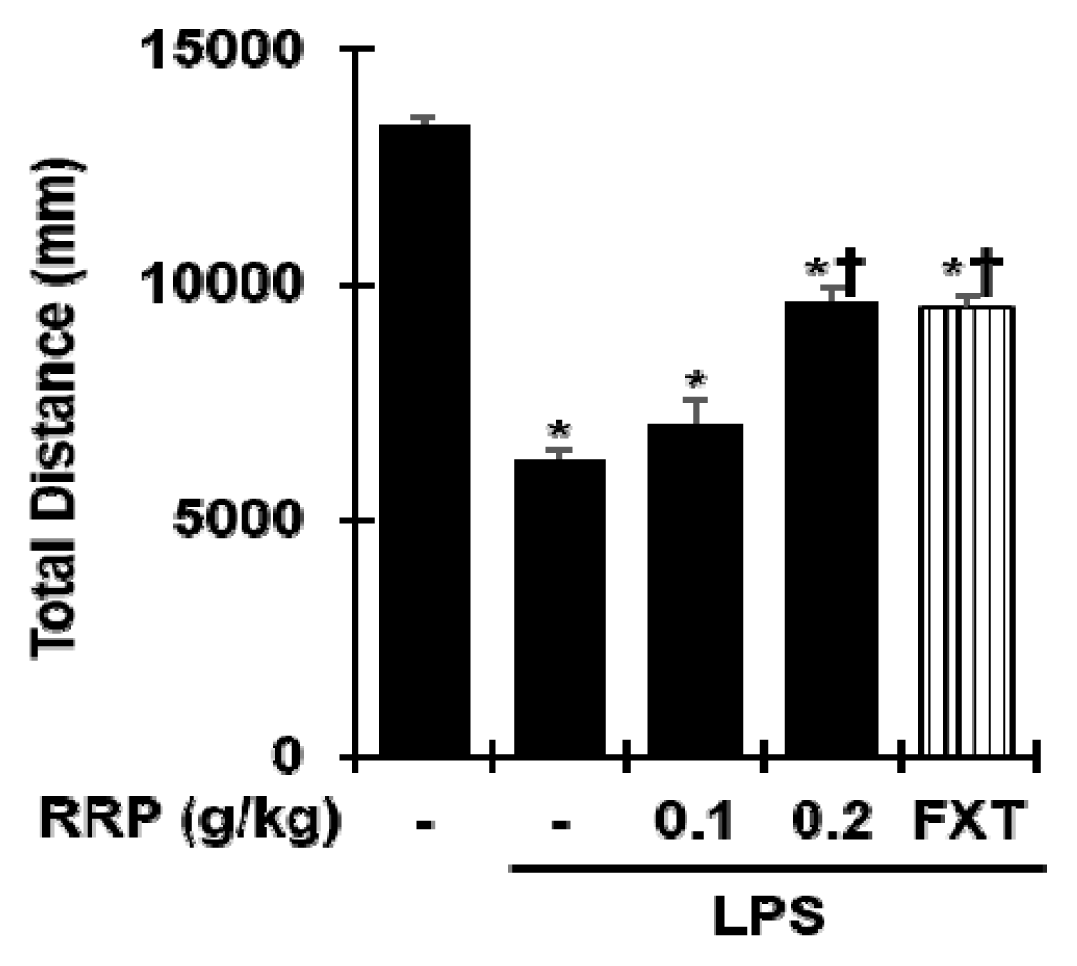
Effect of RRP on Open field test (OFT) in the LPS-induced depressive-like behavior.
Data are the mean ± S.D.(n = 3). *p < 0.05 versus saline, †p < 0.05 versus LPS. RRP: Rehmanniae Radix Preparata, FXT: Fluoxetine.
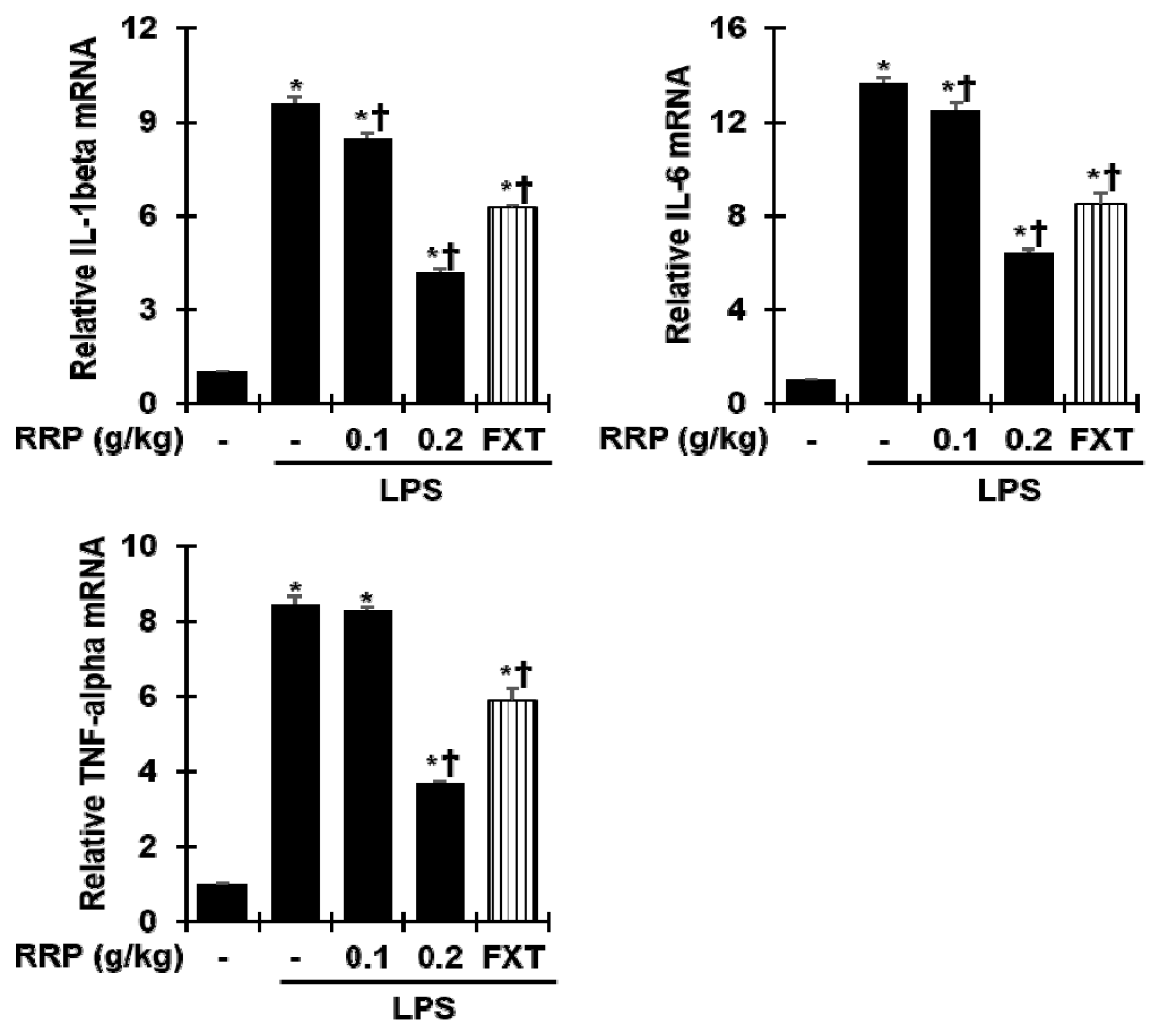
Effect of RRP on inflammatory cytokines in the LPS-induced depressive-like model.
The mRNA expression level of IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α were measured by qPCR. Data are the mean ± S.D.(n = 3). *p< 0.05 versus saline, †p < 0.05 versus LPS. RRP: Rehmanniae Radix Preparata, FXT: Fluoxetine.