References
1. Korean Acupuncture & Moxibustion Medicine Society. 2020. Acupuncture and Moxibustion (admended 1st edth ed. Korea: Hanmi Press.
2. Yao C., Xu Y., Chen L., Jiang H., Ki C.S., Byun J.S., Bian W.. 2016;Effects of warm acupuncture on breast cancer-related chronic lymphedema: a randomized controlled trial. Current Oncology 23(1):27–34.
https://doi.org/10.3747/co.23.2788
.
3. Ko H.J., Yoo J.H., Kim M.W., Shin J.C.. 2020;Systematic Review of Fire Needling or Warm Needling Treatment for Ankle Sprain. J Acupunct Res 27(1):19–27.
https://doi.org/10.13045/jar.2019.00332
.
5. Min W.K., Yeo S., Kim E.H., Song H.S., Koo S., Lee J.D., Lim S.. 2013;Comparison of Warm-Needling and Acupuncture for Knee Osteoarthritis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Kor J Acupunct 30(1):64–72.
6. Li X., Han Y., Cui J., Yuan P., Di Z., Li L.. 2016;Efficacy of warm needle moxibustion on lumbar disc herniation: a meta-analysis. J Evid Based Complementary Altern Med 21(4):311–319.
https://doi.org/10.1177/2156587215605419
.
7. Zhang J., Chen Y., Lan K., Hu L., Yu H.. 2021;Clinical, Anti-hyperuricemic, and Pain-relief Effects of Five Acupuncture and Moxibustion Therapies in Acute Gouty Arthritis: a Network Meta-analysis. Chinese General Practice 24(8):1001.
https://doi.org/10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2020.00.347
.
8. Kim H., Shim I., Yi S.H., Lee H., Lim H.S., Hahm D.H.. 2009;Warm needle acupuncture at Pungsi (GB31) has an enhanced analgesic effect on formalin-induced pain in rats. Brain res bull 78(4–5):164–169.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2008.10.006
.
9. Yang L., Tan J.Y., Ma H., Zhao H., Lai J., Chen J.X., Suen L.K.P.. 2018;Warm-needle moxibustion for spasticity after stroke: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Int J Nurs Stud 82:129–138.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2018.03.013
.
10. o. H.R. , Choi S.K., Sung W.S., Lee S.D., Lee B.W., Kim E.J.. 2022;Thermal Properties of Warm-versus Heated-Needle Acupuncture. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2022;:4159172.
https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/4159172
.
11. Kim J.W., Lee H.J., Ahn C.B., Yi S.H.. 2011;Study of the thermal properties of warm needle and the development of warm needle apparatus. J Acupunct Res 28(1):15–28.
12. Yi S.H., Kang J.W., Nam D.W., Kim E.J., Lee H.J., Kim K.S., Lee J.D.. 2009;Study on the Thermal Properties of Electric Moxibustion Apparatus for Presenting Assessment Guideline in Korea. J Acupunct Res 26(6):31–39.
13. Lee B.W., Oh Y.T., Jang H., Choi S.K., Jo H.R., Sung W.S., Kim E.J.. 2021;An Experimental Study on the Development and Possible Solution of Thermal Runaway Model of Electronic Moxibustion with System Error. Korean J Acupunct 38(4):282–289.
https://doi.org/10.14406/acu.2021.029
.
15. Lee J.H., Jo H.R., Kim S.H., Lee Y.S., Park S.W., Moon S.R., Kim E.J.. 2019;A Review on the Characteristics of Temperature Variation in Warm Needle. J Kor Med 40(3):112–138.
https://doi.org/10.13048/jkm.19031
.
16. Yang S.B., Kwon O.S.. 2019;Principal components of thermal stimulation while the warm needling: diameter of the acupuncture needle and distance from the skin. Kor J Acupunct 36(4):210–220.
https://doi.org/10.14406/acu.2019.024
.
17. Yi S.H., Kang J.W., Nam D.W., Kim E.J., Lee H.J., Kim K.S., Lee J.D.. 2010;Study on Developing Assessment Guideline for Safety and Performance of Electric Moxibustion Apparatus. J Acupunct Res 27(1):75–86.
19. International Organization for Standardization. Traditional Chinese medicine –Electric heating moxibustion equipment (ISO Standard No. 21292:2020) 2020. [cited 2022 Jul 27] Available from URL: from
https://www.iso.org/standard/70470.html
.
20. Yang S.B., Kim M.S., Kim J.H.. 2018;Analgesia of Electroacupuncture and Radio -Frequency Warm Needling in Acupoint Combination on Ankle Sprain in Rats. Kor J Acupunct 35(1):27–35.
https://doi.org/10.14406/acu.2018.005
.
21. Lee S.Y., Byeon S.J., Choi Y.B., Kim J.J., Lee Y.H.. 2016;Clinical Assessment of Warm Acupuncture Therapy System Using HF Time-varying Magnetic Field. Kor J Acupunct 33(4):213–220.
https://doi.org/10.14406/acu.2016.027
.
22. Korean Law Information Center. Common standard for biological safety evaluation of medical devices (ministry of Food and Drug Safety act No. 2020–12) 2020. [cited 2022 Jul 27] Available from URL:
https://law.go.kr
.
23. Korean Law Information Center. Common standard and testing methods for electrical safety evaluation of medical devices (ministry of Food and Drug Safety act No. 2015–115) 2015. Available from URL:
https://law.go.kr
.
24. Korean Law Information Center. Common standard for electromagnetic safety evaluation of medical devices (ministry of Food and Drug Safety act No. 2020–29) 2020. [cited 2022 Jul 27] Available from URL:
https://law.go.kr
.
25. Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service. HIRA charging method and reimbursement standards – I.Acting-chapter13,14 Korean traditional medicine examination, and treatment 2009. [cited 2022 Jul 27]. Available from URL:
http://rulesvc.hira.or.kr/
.
26. Chung J.Y., Choi D.Y., Woo H.S., Kang S.K.. 2009;Review of clinical trials on warming acupuncture for musculoskeletal pain diseases-A systematic review. J Acupunct Res 26(4):11–18.
27. Luo D. Jr, Liu Y. Jr, Wu Y. Jr, Ma R. Jr, Wang L. Jr, Gu R. Jr, Fu W. Sr. 2018;Warm needle acupuncture in primary osteoporosis management: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Acupuncture in Medicine 36(4):215–221.
https://doi.org/10.1136/acupmed-2016-011227
.
28. Liu G.F., Gao Z., Liu Z.N., Yang M., Zhang S., Tan T.P.. 2021;Effects of warm needle acupuncture on temporomandibular joint disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2021;
https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6868625
.
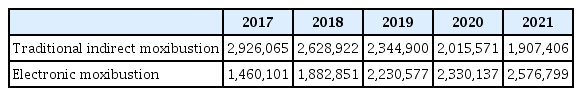
29. Kim D.J., Jo H.R., Jang H., Choi S.K., Jung C.Y., Sung W.S., Kim E.J.. 2022;Temperature Characteristics of Traditional Indirect Moxibustion and Electronic Moxibustion. J Acupunct Meridian Stud 15(3):174–180.
https://doi.org/10.51507/j.jams.2022.15.3.174
.
30. Chung H.J., Rhee K.Y.. 2009;Coating of heat-acupuncture needle using an Al2O3 material to improve a heat insulation. J. Korean Soc. Precis. Eng 26(4):114–119.
32. Zhang D., Das D.B., Rielly C.D.. 2014;Microneedle assisted micro-particle delivery from gene guns: experiments using skin-mimicking agarose gel. J Pharm Sci 103(2):613–627.
https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.23835
.
33. Fujii M., Yamanouchi S., Hori N., Iwanaga N., Kawaguchi N., Matsumoto M.. 1997;Evaluation of Yucatan micropig skin for use as an in vitro model for skin permeation study. Biol Pharm Bull 20(3):249–254.
https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.20.249
.