References
3. Koh NY, Kim CG, Ko YS, Lee JH. 2015;Acupuncture Treatment of Plantar Fasciitis: A Literature Review. J Korean Med Rehabil 25(2):97–110.
4. Ha WB. 2022;A Case Report of Talipes Cavus-Type Plantar Fasciitis Treated with Acupotomy and Fascia Chuna Therapy. The Journal of Korea Chuna Manual Medicine for Spine & Nerves 17(1):47–53.
https://doi.org/10.30581/jcmm.2022.17.1.47
.
5. Hwang HJ, Lee KJ, Park YH, Keum DH. 2008;Two Clinical Cases on Plantar Fasciitis Using Myofascial Releasing Therapy and Acupuncture Therapy. J Korean Med Rehabil 18(2):111–118.
7. Ahn KH, Kim KH, Hwang HS, Song HS, Kwon SJ, Lee SN, et al. 2002;The Effect of Bee-venom Acupuncture on Heel Pain. The Journal of Korean Acupuncture & Moxibustion Society 19(5):149–160.
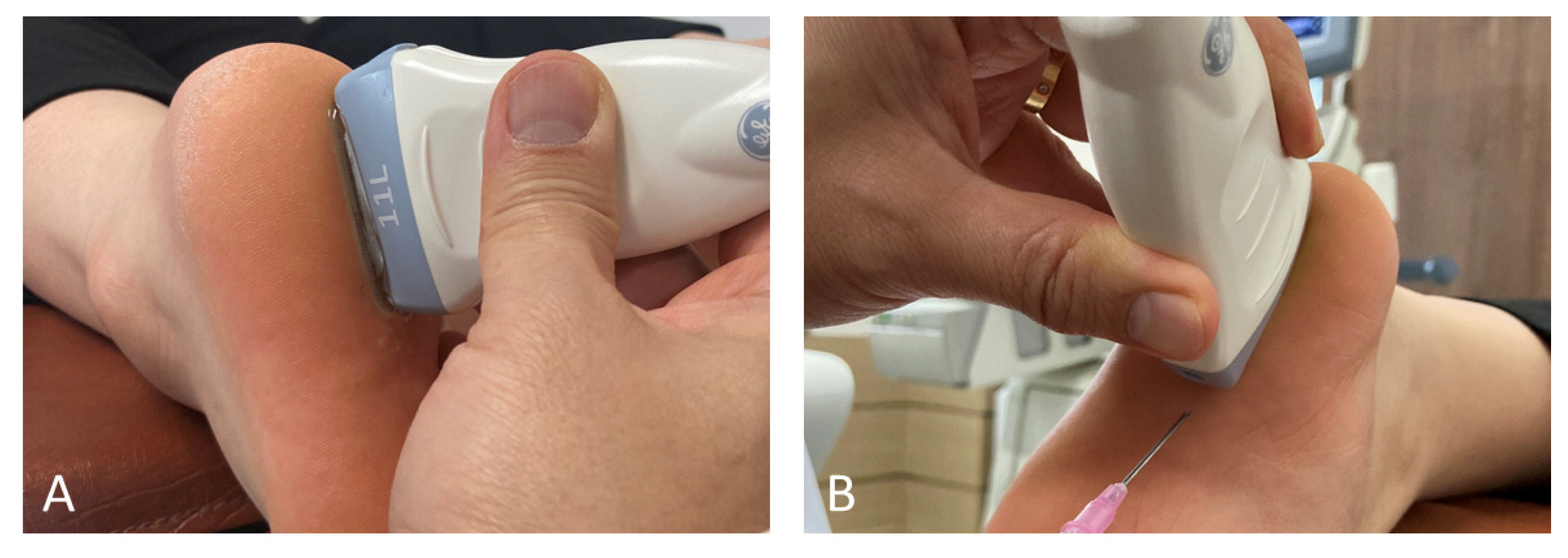
8. Lee SJ, Ki SH, Koh DK, Lee SH, Lim HH, Song YK. 2022;A Study on the Exploration of Treatment Area of Visceral Chuna Manual Therapy Using Ultrasound Image Data. J Korean Med Rehabil 32(2):139–154.
https://doi.org/10.18325/jkmr.2022.32.2.139
.
9. Ahn TS, Moon JH, Park CY, Oh MJ, Choi YM. 2019;The Effectiveness of Ultrasound-Guided Essential Bee Venom Pharmacopuncture Combined with Integrative Korean Medical Treatment for Rib Fracture: A Case Study. J Korean Med Rehabil 29(3):157–163.
https://doi.org/10.18325/jkmr.2019.29.3.157
.
10. Kim YH, Oh TY, Lee EJ, Oh MS. 2019;A Comparative Study on the Pain and Treatment Satisfaction between Korean Medical Treatment Combined with Ultrasound Guided Soyeom Pharmacopuncture Therapy in Thoracic Paravertebral Space and Non-Guided Soyeom Pharmacopuncture Therapy on Patients with Ribs Fracture: A Retrospective Study. J Korean Med Rehabil 29(3):103–112.
https://doi.org/10.18325/jkmr.2019.29.3.103
.
11. Kim SW, Jeon DH, Kim BJ, Park JW, Oh MS. 2021;The Effectiveness of Ultrasound-Guided Soyeom Pharmacopuncture Therapy at Acromioclavicular Joint of Shoulder in Patients with Anterior Shoulder Pain: A Retrospective Study. J Korean Med Rehabil 31(3):95–104.
https://doi.org/10.18325/jkmr.2021.31.3.95
.
12. Jeong JK, Park GN, Kim KM, Kim SY, Kim ES, Kim JH, et al. 2016;The Effectiveness of Ultrasound-guided Bee Venom Pharmacopuncture Combined with Integrative Korean Medical Treatment for Rotator cuff Diseases : A Retrospective Case Series. The Acupuncture 33(4):165–180.
https://doi.org/10.13045/acupunct.2016063
.
13. Yang JE, Oh MS. 2022;Comparison of Ultrasound Guided Soyeom Pharmacopuncture Therapy Effect and Unguided Soyeom Pharmacopuncture Therapy Effect on Cervical Facet Joint of Acute Cervical Pain Patient Caused by Traffic Accidents: A Retrospective Study. J Korean Med Rehabil 32(3):109–117.
https://doi.org/10.18325/jkmr.2022.32.3.109
.
14. Park JW, Kim SW, Jeon DH, Kim BJ, Oh MS. 2021;Comparison the Soyeom Pharmacopuncture Therapy Effects of Ultrasound Guided Group and Unguided Group on the Patients’ Facet Joint with Acute Low Back Pain Caused by Traffic Accidents: A Retrospective Study. J Korean Med Rehabil 31(3):85–93.
https://doi.org/10.18325/jkmr.2021.31.3.85
.
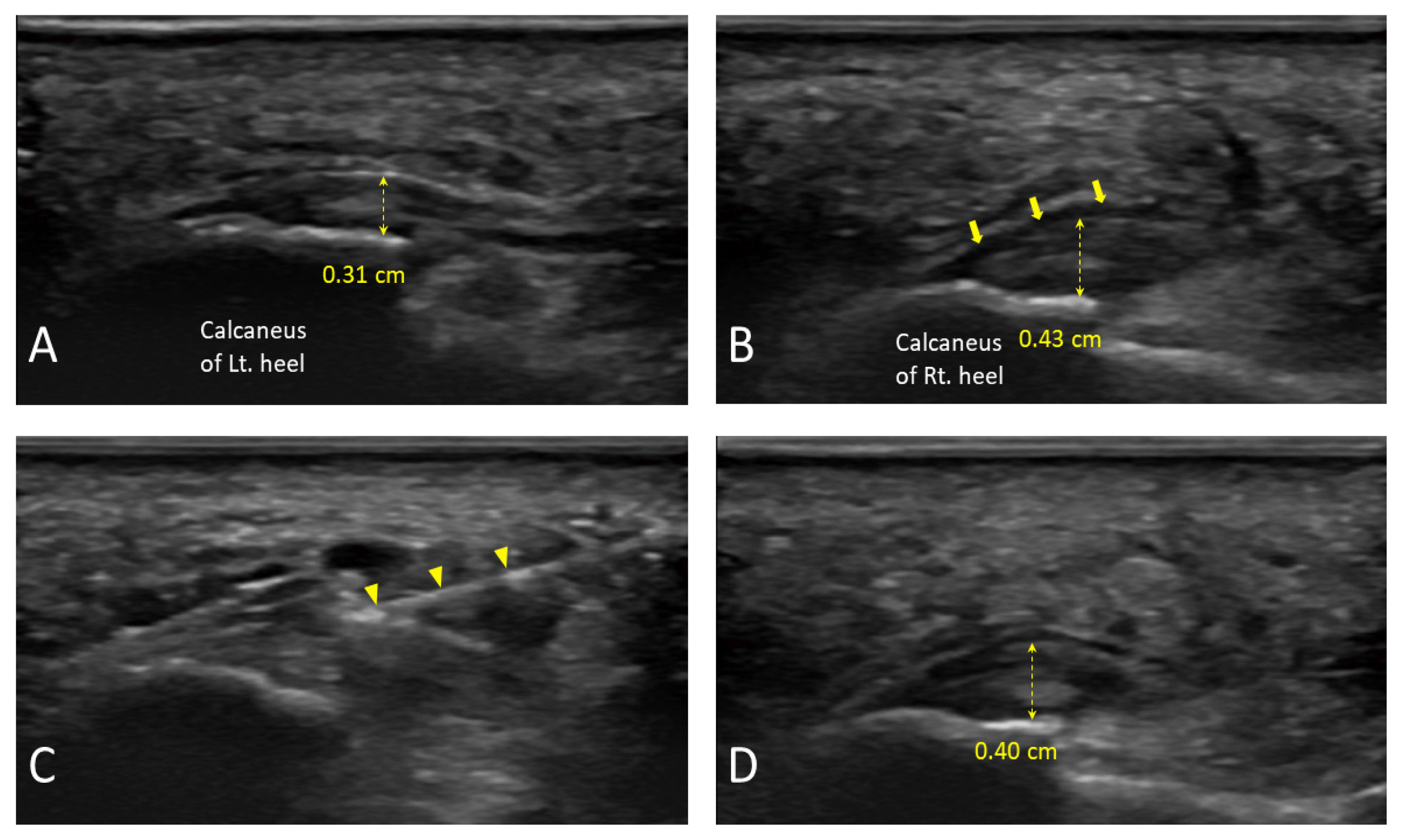
15. Hong SH, Chu IT, Chung HW. 2007;Ultrasonographic Appearances of the Plantar Fasciitis. J Korean Foot Ankle Soc 11(2):145–148.
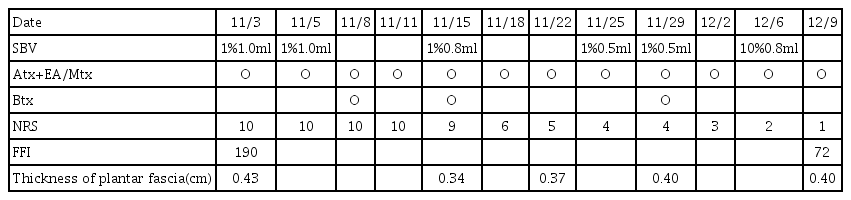
16. Breivik H, Borchgrevink PC, Allen SM, Rosseland LA, Romundstad L, Breivik Hals EK, et al. 2008;Assessment of pain. British Journal of Anaesthesia 101:17–24.
https://10.1093/bja/aen103
.
18. Thomas JL, Christensen JC, Kravitz SR, Mendicino RW, Schuberth JM, Vanore JV, et al. 2010;The diagnosis and treatment of heel pain: a clinical practice guideline-revision 2010. J Foot Ankle Surg 49(3 Suppl):S1–19.
https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jfas.2010.01.001
.
19. Barrett SES. 2004;Growth factors for chronic plantar fascitis. Podiatry Today 17:37–42.
21. Li Z, Yu A, Qi B, Zhao Y, Wang W, Li P, et al. 2015;Corticosteroid versus placebo injection for plantar fasciitis: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Exp Ther Med 9:2263–8.
https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2015.2384
.
22. Jo OY, Moon HR, Yang JM, Yoon MJ, Lee JY, Jang KJ, et al. 2021;A case report of Plantar fasciitis treated by Western and Korean medical treatment including Bee venom pharmacopuncture. Journal of the Spine&joint Korean Medicine 18(1):171–181.
23. Baik TH. 2014;Using Ultrasonography in Korean Medicine to Observe Organs and Diseases, and Evidence of its Use. J Korean Med 35(3):70–92.
https://doi.org/10.13048/jkm.14032
.
24. Lee SH. 2021;Prospects for the Development of Acupuncture Treatment Led by the Use of Ultrasound Imaging Devices. Journal of Korean Medical Society of Soft Tissue 5(1):8–11.
https://doi.org/10.54461/JKMST.2021.5.1.8
.